Page 472 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 472
448 19 Chemoenzymatic Multistep One-Pot Processes
The Heck reaction as another type of palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reaction
was also combined with a subsequent enzymatic ketone reduction. In their initial
work, Cacchi et al. [64] conducted a Heck reaction of an aryliodide with butanone
in organic media, and used the crude product obtained after removal of the volatile
components directly for a subsequent biocatalytic reduction. The ADH turned out
to be compatible with this crude product, and the desired allylic alcohols were
obtained in yields of up to 85% and with >99% ee in all cases.
The development of a Heck reaction in aqueous media, enabling a one-pot
process with both reaction steps (Heck reaction and biotransformation) running
in aqueous media, was also reported by Cacchi and coworkers [65]. This type of
Heck reaction is based on the use of a phosphine-free perfluoro-tagged palladium
nanoparticle. After detailed catalyst characterization and process development,
Cacchi and coworkers also succeeded in combining this Heck reaction efficiently
with the subsequent asymmetric ketone reduction toward a one-pot process. A
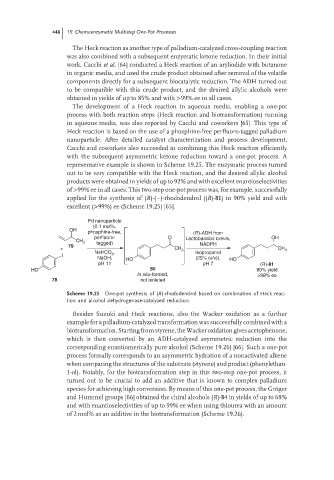
representative example is shown in Scheme 19.25. The enzymatic process turned
out to be very compatible with the Heck reaction, and the desired allylic alcohol
products were obtained in yields of up to 92% and with excellent enantioselectivities
of >99% ee in all cases. This two-step one-pot process was, for example, successfully
applied for the synthesis of (R)-(−)-rhododendrol ((R)-81) in 90% yield and with
excellent (>99%) ee (Scheme 19.25) [65].
Pd nanoparticle
(0.1 mol%,
OH
phosphine-free, (R)-ADH from
perfluoro- O Lactobacillus brevis, OH
CH 3 tagged)
79 NADPH
+ CH 3 CH 3
NaHCO , Isopropanol
I 3
NaOH, HO (25% (v/v)), HO
pH 11 pH 7 (R)-81
HO 80 90% yield
In situ-formed, >99% ee
78 not isolated
Scheme 19.25 One-pot synthesis of (R)-rhododendrol based on combination of Heck reac-
tion and alcohol dehydrogenase-catalyzed reduction.
Besides Suzuki and Heck reactions, also the Wacker oxidation as a further
example for a palladium-catalyzed transformation was successfully combined with a
biotransformation. Starting from styrene, the Wacker oxidation gives acetophenone,
which is then converted by an ADH-catalyzed asymmetric reduction into the
corresponding enantiomerically pure alcohol (Scheme 19.26) [66]. Such a one-pot
process formally corresponds to an asymmetric hydration of a nonactivated alkene
when comparing the structures of the substrate (styrene) and product (phenylethan-
1-ol). Notably, for the biotransformation step in this two-step one-pot process, it
turned out to be crucial to add an additive that is known to complex palladium
species for achieving high conversion. By means of this one-pot process, the Gr¨ oger
and Hummel groups [66] obtained the chiral alcohols (R)-84 in yields of up to 68%
and with enantioselectivities of up to 99% ee when using thiourea with an amount
of 2 mol% as an additive in the biotransformation (Scheme 19.26).