Page 148 - Biomedical Engineering and Design Handbook Volume 2, Applications
P. 148
DESIGN OF RESPIRATORY DEVICES 127
8
7
6
5
Volume (L) 4 FVC
3 FEV 1
2
1 1 s
0
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18
Time (s)
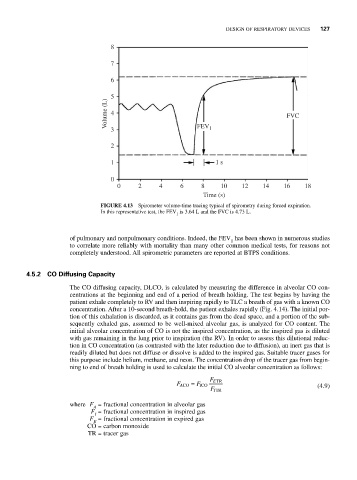
FIGURE 4.13 Spirometer volume-time tracing typical of spirometry during forced expiration.
In this representative test, the FEV is 3.64 L and the FVC is 4.73 L.
1
of pulmonary and nonpulmonary conditions. Indeed, the FEV has been shown in numerous studies
1
to correlate more reliably with mortality than many other common medical tests, for reasons not
completely understood. All spirometric parameters are reported at BTPS conditions.
4.5.2 CO Diffusing Capacity
The CO diffusing capacity, DLCO, is calculated by measuring the difference in alveolar CO con-
centrations at the beginning and end of a period of breath holding. The test begins by having the
patient exhale completely to RV and then inspiring rapidly to TLC a breath of gas with a known CO
concentration. After a 10-second breath-hold, the patient exhales rapidly (Fig. 4.14). The initial por-
tion of this exhalation is discarded, as it contains gas from the dead space, and a portion of the sub-
sequently exhaled gas, assumed to be well-mixed alveolar gas, is analyzed for CO content. The
initial alveolar concentration of CO is not the inspired concentration, as the inspired gas is diluted
with gas remaining in the lung prior to inspiration (the RV). In order to assess this dilutional reduc-
tion in CO concentration (as contrasted with the later reduction due to diffusion), an inert gas that is
readily diluted but does not diffuse or dissolve is added to the inspired gas. Suitable tracer gases for
this purpose include helium, methane, and neon. The concentration drop of the tracer gas from begin-
ning to end of breath holding is used to calculate the initial CO alveolar concentration as follows:
F ACO = F ICO F ETR (4.9)
F ITR
where F = fractional concentration in alveolar gas
A
F = fractional concentration in inspired gas
I
F = fractional concentration in expired gas
E
CO = carbon monoxide
TR = tracer gas