Page 129 - Cam Design Handbook
P. 129
THB5 8/15/03 1:52 PM Page 117
CAM MOTION SYNTHESIS USING SPLINE FUNCTIONS 117
1
0
Displacement (cm)
Velocity (cm/rad)
Acceleration (cm/rad/rad)
Constraint
–1
0 45 90 135 180
Cam rotation angle (deg)
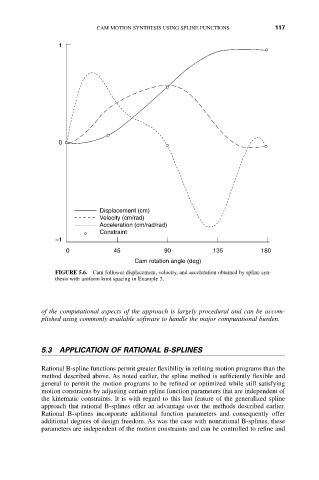
FIGURE 5.6. Cam follower displacement, velocity, and acceleration obtained by spline syn-
thesis with uniform knot spacing in Example 3.
of the computational aspects of the approach is largely procedural and can be accom-
plished using commonly available software to handle the major computational burden.
5.3 APPLICATION OF RATIONAL B-SPLINES
Rational B-spline functions permit greater flexibility in refining motion programs than the
method described above. As noted earlier, the spline method is sufficiently flexible and
general to permit the motion programs to be refined or optimized while still satisfying
motion constraints by adjusting certain spline function parameters that are independent of
the kinematic constraints. It is with regard to this last feature of the generalized spline
approach that rational B-splines offer an advantage over the methods described earlier.
Rational B-splines incorporate additional function parameters and consequently offer
additional degrees of design freedom. As was the case with nonrational B-splines, these
parameters are independent of the motion constraints and can be controlled to refine and