Page 74 - Cam Design Handbook
P. 74
THB3 8/15/03 12:58 PM Page 62
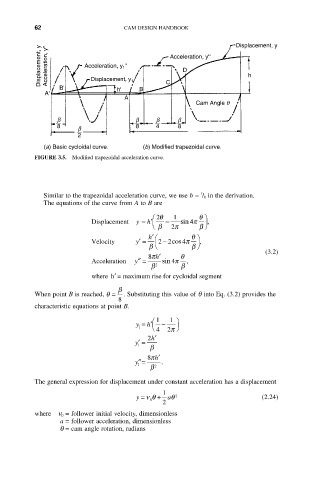
62 CAM DESIGN HANDBOOK Displacement, y
Displacement, y Acceleration, y'' Acceleration, y 1 '' Acceleration, y'' h
D
B' Displacement, y 1 B C
h'
A'
A
Cam Angle q
b b b b
8 b 8 4 8
2
(a) Basic cycloidal curve. (b) Modified trapezoidal curve.
FIGURE 3.5. Modified trapezoidal acceleration curve.
1
Similar to the trapezoidal acceleration curve, we use b = / 8 in the derivation.
The equations of the curve from A to B are
Ê 2q 1 q ˆ
Displacement y = h¢Á - sin 4p ˜,
Ë b 2p b ¯
h¢ Ê q ˆ
Velocity y¢ = Á22 4p ˜,
- cos
b Ë b ¯
(3.2)
p
8 h¢ q
Acceleration y¢¢ = sin 4p ,
b 2 b
where h = maximum rise for cycloidal segment
¢
b
When point B is reached, q = . Substituting this value of q into Eq. (3.2) provides the
8
characteristic equations at point B.
Ê 1 1 ˆ
y = h¢ Ë 4 - 2p ¯
1
2 h¢
y¢ =
1
b
8p h¢
y¢¢= .
1
b 2
The general expression for displacement under constant acceleration has a displacement
1
y = nq + aq 2 (2.24)
0
2
where n 0 = follower initial velocity, dimensionless
a = follower acceleration, dimensionless
q = cam angle rotation, radians