Page 89 - Cam Design Handbook
P. 89
THB3 8/15/03 12:58 PM Page 77
MODIFIED CAM CURVES 77
the beginning of motion, point B the end of motion, and point P the mid-stroke
transition point. APB is the constant velocity line. M is the midpoint between A and
P. The sine amplitudes are added to the constant-velocity line in this true cycloidal
case.
The modified cycloidal curve was developed to maximize the orientation of the
superimposed sine wave amplitude on the straight line; see geometric construction in
b
Fig. 3.12b. In this figure, a point D equal to 0.57 the distance is the first chosen and
2
then is joined to M by a straight line. The base of the sine curve is then constructed
Distance of Center of Radially Translating Roller Follower from Center of Cam 4.0
5.0
4.8
y Displacement (in) 4.6
4.4
4.2
3.8
3.6
3.4
3.2
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
Cam rotation (deg)
(a) Displacement.
18
16
14
y Velocity (in./sec.) 12
10
. 8
6
4
2
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
Cam rotation (deg)
(b) Velocity.
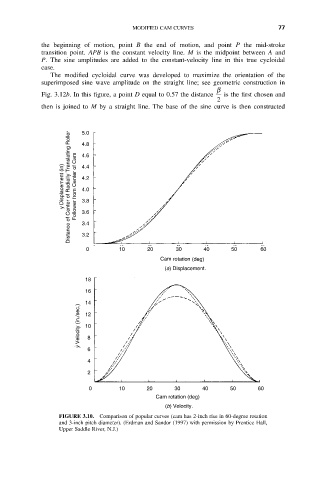
FIGURE 3.10. Comparison of popular curves (cam has 2-inch rise in 60-degree rotation
and 3-inch pitch diameter). (Erdman and Sandor (1997) with permission by Prentice Hall,
Upper Saddle River, N.J.)