Page 132 - Chemical Process Equipment - Selection and Design
P. 132
104 FLOW OF FLUIDS
/==+*:
...........................
...........................
...........................
.:::::A:: .................
..........
F+/F/+. ................
........
......................
..........................
.................
.....................
........................
..........................
:
.::::::A: : : : : : : : : : : : : :
:
.:z::::::::::::::::::::...
....................... :.
....... ........................ U?
7
eBingham plastic
-----.
E
- 3
Deformation rate Idu/dyl
(b)
Shearing stress -
(e)
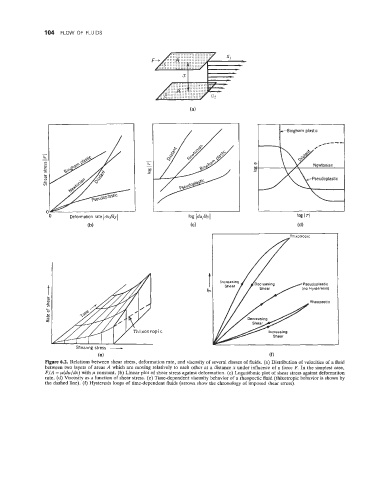
Figure 6.2. Relations between shear stress, deformation rate, and viscosity of several classes of fluids. (a) Distribution of velocities of a fluid
between two layers of areas A which are moving relatively to each other at a distance x under influence of a force F. In the simplest case,
F/A = y(du/dx) with y constant. (b) Linear plot of shear stress against deformation. (c) Logarithmic plot of shear stress against deformation
rate. (d) Viscosity as a function of shear stress. (e) Time-dependent viscosity behavior of a rheopectic fluid (thixotropic behavior is shown by
the dashed line). (f) Hysteresis loops of time-dependent fluids (arrows show the chronology of imposed shear stress).