Page 133 - Chemical Process Equipment - Selection and Design
P. 133
6.6. NON-NEMrFONlAN LIQUIDS 105
opposite those of pseudoplastics insofar as viscosity behavior is yield-pseudoplastics exist. For instance, data from the literature of a
concerned. The z-j plots are concave upward and the power law 20% clay in water suspension are represented by the numbers
applies zo = 7.3 dyn/cm2, K = 1.296 dyn(sec)"/cm2 and IZ = 0.483 (Govier
and Aziz, 1972, p. 40). Solutions of 0.5-5.0% carboxypolymethylene
z=Kj", n>l, (6.38) also exhibit this kind of behavior, but at lower concentrations the yield
stress is zero.
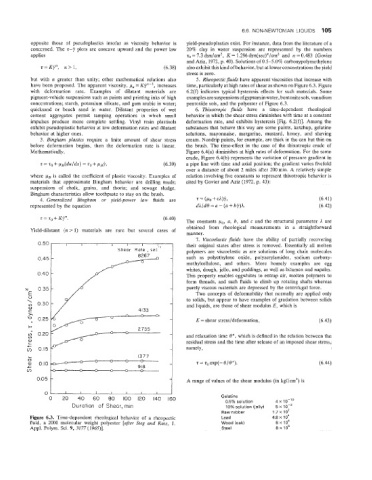
but with n greater than unity; other mathematical relations also 5. Rheopectic fluids have apparent viscosities that increase with
have been proposed. The apparent viscosity, pa = KjY-', increases time, particularly at high rates of shear as shown on Figure 6.3. Figure
with deformation rate. Examples of dilatant materials are 6.2(f) indicates typical hysteresis effects for such materials. Some
pigment-vehicle suspensions such as paints and printing inks of high examples are suspensions of gypsum in water, bentonite sols, vanadium
concentrations; starch, potassium silicate, and gum arabic in water; pentoxide sols, and the polyester of Figure 6.3.
quicksand or beach sand in water. Dilatant properties of wet 6. Thixotropic fluids have a time-dependent rheological
cement aggregates permit tamping operations in which small behavior in which the shear stress diminishes with time at a constant
impulses produce more complete settling. Vinyl resin plastisols deformation rate, and exhibits hysteresis [Fig. 6.2(f)]. Among the
exhibit pseudoplastic behavior at low deformation rates and dilatant substances that behave this way are some paints, ketchup, gelatine
behavior at higher ones. solutions, mayonnaise, margarine, mustard, honey, and shaving
3. Bingham plastics require a finite amount of shear stress cream. Nondrip paints, for example, are thick in the can but thin on
before deformetion begins, then the deformation rate is linear. the brush. The time-effect in the case of the thixotropic crude of
Mathematically, Figure 6.4(a) diminishes at high rates of deformation. For the same
crude, Figure 6.4(b) represents the variation of pressure gradient in
t = zo + pu(duJdx) = to + puj, (6.39) a pipe line with time and axial position; the gradient varies fivefold
over a distance of about 2 miles after 200 win. A relatively simple
where pB is called the coefficient of plastic viscosity. Examples of relation involving five constants to represent thixotropic behavior is
materials that approximate Bingham behavior are drilling muds; cited by Govier and Aziz (1972, p. 43):
suspensions of chalk, grains, and thoria; and sewage sludge.
Bingham characteristics allow toothpaste to stay on the brush.
4. Generahzed Bingham or yield-power law fluids are (6.41)
represented by the equation (6.42)
t = to + K?". (6.40) The constants po, a, b, and c and the structural parameter 11 are
obtained from rheological measurements in a straightforward
Yield-dilatant (n > 1) materials are rare but several cases of
manner.
7. Viscoelastic fluids have the ability of partially recovering
their original states after stress is removed. Essentially all molten
polymers are viscoelastic as are solutions of long chain molecules
such as polyethylene oxide, polyacrylamides, sodium carboxy-
methylcellulose, and others. More homely examples are egg
whites, dough, jello, and puddings, as well as bitumen and napalm.
This property enables eggwhites to entrap air, molten polymers to
form threads, and such fluids to climb up rotating shafts whereas
purely viscous materials are depressed by the centrifugal force.
Two concepts of deformability that normally are applied only
to solids, but appear to have examples of gradation between solids
and liquids, are those of shear modulus E, which is
E = shear stress/deformation, (6.43)
and relaxation time 8*, which is defined in the relation between the
residual stress and the time after release of an imposed shear stress,
namely,
z= zoexp(-8/8*). (6.44)
0.05 A range of values of the shear modulus (in kgf/cm2) is
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 Gelatine 4 x 10-10
0.5% solution
Duration of Shear, mln 10% solution (jelly) 5 x ?o-*
Raw rubber 1.7 X 10'
Figure 6.3. Time-dependent rheological behavior of a rheopectic Lead 4.8 x io4
fluid, a 2000 molecular weight polyester [after Steg and Katz, J. Wood (oak) 8x1~4
Appl. Polym. Sci. 9, 3177(1965)]. Steel 8x30~