Page 169 - Chemical Process Equipment - Selection and Design
P. 169
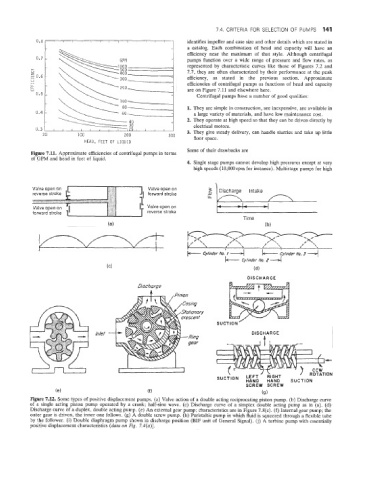
7.4. CRITERIA FOR SELECTION OF PUMPS 141
identifies impeller and case size and other details which are stated in
a catalog. Each combination of head and capacity will have an
i efficiency near the maximum of that style. Although centrifugal
GPM pumps function over a wide range of pressure and $~QW rates, as
represented by characteristic curves like those of Figures 7.2 and
7.7, they are often characterized by their performance ab the peak
efficiency, as stated in the previous section. Approximate
efficiencies of centrifugal pumps as functions of head and capacity
are on Figure 7.11 and elsewhere here.
Centrifugal pumps have a number of good qualities:
1. They are simple in construction, are inexpensive. are available in
a large variety of materials, and have low maintenance cost.
2. They operate at high speed so that they can be driven directly by
electrical motors.
3. They give steady delivery, can handle slurHies and take up little
20 100 200 300 floor space.
HEAD, FEET OF LIOUID
Some of their drawbacks are
Figure 7.11. Approximate efficiencies of centrifugal pumps in terms
of GPM and head in feet of liquid.
4. Single stage pumps cannot develop high pressures except at very
high speeds (10,000 rpm for instance). Multistage pumps for high
Valve open on 3
0
reverse stroke forward stroke ti
Valve open on
reverse stroke
Time
(a) (b)
(C)
Discharge
SUCTION
DISCHARGE
A
SCREW SCREW
(e) (b
Figure 7.U. Some types of positive displacement pumps. (a) Valve action of a double acting reciprocating piston pump. (b) Discharge curve
of a single acting piston pump operated by a crank; half-sine wave. (c) Discharge curve of a simplex double acting pump as in (a). (d)
Discharge curve of a duplex, double acting pump. (e) An external gear pump; characteristics are in Figure 7.8(c). (f) Internal gear pump; the
outer gear is driven, the inner one follows. (8) A double screw pump. (h) Peristaltic pump in which fluid is squeezed through a flexible tube
by the follower. (i) Double diaphragm pump shown in discharge position (BIF unit of General Signal). (j) A turbine pump with essentially
positive displacement characteristics (data on Fig. 7.4(a)].