Page 168 - Chemical Process Equipment - Selection and Design
P. 168
140 FLUID TRANSPORT EQUIPMENT
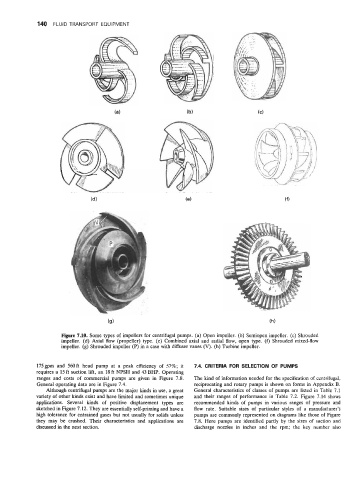
Figure 7.10. Some types of impellers for centrifugal pumps. (a) Open impeller. (b) Semiopen impeller. (c) Shrouded
impeller. (d) Axial flow (propeller) type. (e) Combined axial and radial flow, open type. (f) Shrouded mixed-flow
impeller. (g) Shrouded impeller (P) in a case with diffuser vanes (V). (h) Turbine impeller.
175gpm and 560ft head pump at a peak efficiency of 57%; it 7.4. CRITERIA FOR SELECTION OF PUMPS
requires a 15 ft suction lift, an 18 ft NPSH and 43 BHP. Operating
ranges and costs of commercial pumps are given in Figure 7.8. The kind of information needed for the specification of centrifugal,
General operating data are in Figure 7.4. reciprocating and rotary pumps is shown on forms in Appendix B.
Although centrifugal pumps are the major kinds in use, a great General characteristics of classes of pumps are listed in Table 7.1
variety of other kinds exist and have limited and sometimes unique and their ranges of performance in Table 7.2. Figure 7.14 shows
applications. Several kinds of positive displacement types are recommended kinds of pumps in various ranges of pressure and
sketched in Figure 7.12. They are essentially self-priming and have a flow rate. Suitable sues of particular styles of a manufacturer’s
high tolerance for entrained gases but not usually for solids unless pumps are commonly represented on diagrams like those of Figure
they may be crushed. Their characteristics and applications are 7.8. Here pumps are identified partly by the sizes of suction and
discussed in the next section. discharge nozzles in inches and the rpm; the key number also