Page 242 - Chemical Process Equipment - Selection and Design
P. 242
212 HEAT TRANSFER AND HEAT EXCHANGERS
The heat is transferred by direct radiation and convection and also tubes because the higher convection transfer counteracts the lesser
by reflection from refractory walls lining the chamber. radiation due to lack of refractory wall backing. Accordingly, shield
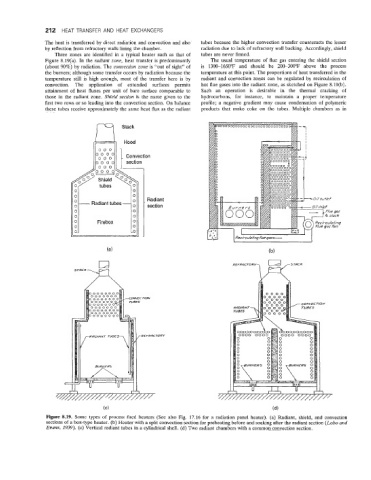
Three zones are identified in a typical heater such as that of tubes are never finned.
Figure 8.19(a). In the radiant zone, heat transfer is predominantly The usual temperature of flue gas entering the shield section
(about 90%) by radiation. The convection zone is “out of sight” of is 1300-1650°F and should be 200-300°F above the process
the burners; although some transfer occurs by radiation because the temperature at this point. The proportions of heat transferred in the
temperature still is high enough, most of the transfer here is by radiant and convection zones can be regulated by recirculation of
convection. The application of extended surfaces permits hot flue gases into the radiant zone, as sketched on Figure 8.19(b).
attainment of heat fluxes per unit of bare surface comparable to Such an operation is desirable in the thermal cracking of
those in the radiant zone. Shield section is the name given to the hydrocarbons, for instance, to maintain a proper temperature
first two rows or so leading into the convection section. On balance profile; a negative gradient may cause condensation of polymeric
these tubes receive approximately the same heat flux as the radiant products that make coke on the tubes. Multiple chambers as in
Stack
000
tubes
Radiant
section
(a)
A
5T#CK
r REFRACTORY
c
///// ///’/////A r‘ b- 7’ ////////////////
(C) (d)
Figure 8.19. Some types of process fired heaters (See also Fig. 17.16 for a radiation panel heater). (a) Radiant, shield, and convection
sections of a box-type heater. (b) Heater with a split convection section for preheating before and soaking after the radiant section (Lobo and
Evans, 1939). (c) Vertical radiant tubes in a cylindrical shell. (d) Two radiant chambers with a common convection section.