Page 299 - Chemical Process Equipment - Selection and Design
P. 299
9.9. FLUIDIZED BED DRYERS 263
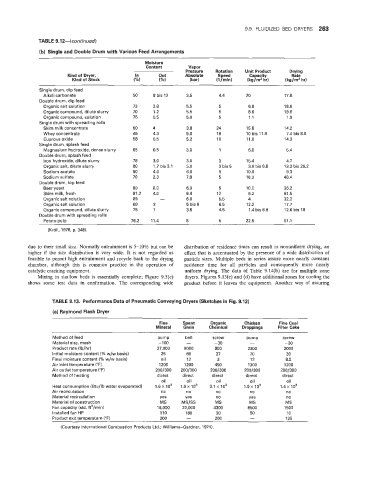
TABLE 9.124 continued)
1 Single ;and Double Drum with Various Feed Arrangements
Moisture
Content Vapor
Pressure
Kind of Dryer, In out Absolute Rotation Unit Product Drying
Rate
Capacity
Speed
Kind of Stock (%I (%I (bar) (l/rnin) (kg/m2 hr) (Wm2 hr)
Single drum, dip feed
Alkali carbonate 50 8 bis 12 3.5 4.4 20 17.8
Double drum, dip feed
Organic salt solution 73 2.8 5.5 5 6.8 18.6
Organic compound, dilute slurry 70 1.2 5.5 5 8.6 19.6
Organic compound, solution 75 0.5 5.0 5 1.1 1.9
Single drum with spreading rolls
Skim milk concentrate 50 4 3.8 24 15.8 14.2
Whey concentrate 45 4.3 5.0 16 10 bis 11.8 7.4 bis 8.8
Cuprous oxide 58 0.5 5.2 10 11.0 14.3
Single drum, splash feed
Magnesium hydroxide, dense slurry 65 0.5 3.0 1 6.8 5.4
Double drum, splash feed
Iron hydroxide, dilute slurry 78 3.0 3.0 3 15.4 4.7
Organic sailt, dilute slurry 80 1.7 bis 3.1 5.0 3 bis 5 3.6 bis 6.8 13.3 bis 26.2
Sodium acetate 50 4.0 6.0 5 10.0 9.3
Sodium sulfate 70 2.3 7.8 5 18.0 40.4
Double drum, top feed
Beer yeast 80 8.0 6.0 5 10.0 36.2
Skim milk. fresh 91.2 4.0 6.4 12 6.2 61.5
Organic salt solution 89 - 6.0 5.5 4 32.3
Organic salt solution 60 3 5 bis 6 6.5 12.2 17.7
Organic compound, dilute slurry 75 1 3.5 4.5 1.4 bis 6.8 12.6 bis 18
Double drum with spreading rolls
Potato pulp 76.2 11.4 8 5 22.5 61.8
(Kroll, 11378, p. 348).
due to their small size. Normally entrainment is 5-10% but can be distribution of residence times can result in nonuniform drying, an
higher if the size distribution is very wide. It is not regarded as effect that is accentuated by the presence of a wide distribution of
feasible to permit high entrainment and recycle back to the drying particle sizes. Multiple beds in series assure more nearly constant
chamber, although this is common practice in the operation of residence time for all particles and consequently more nearly
catalytic cracking equipment. uniform drying. The data of Table 9.14(b) are for multiple zone
Mixing in shallow beds is essentially complete; Figure 9.5(c) dryers. Figures 9.13(c) and (d) have additional zones for cooling the
shows some test data in confirmation. The corresponding wide product before it leaves the equipment. Another way of assuring
.?3. Performance Data of Pneumatic Conveying Dryers (Sketches in Fig. 9.12)
(a) Riiyrnond Flash Dryer
Fine Spent Organic Chicken Fine Coal
Mineral Grain Chemical Droppings Filter Cake
Method of feed pump belt screw pump screw
Material size, mesh -100 - -30 - -30
Product rate (lb/hr) 27,000 9000 900 2300 2000
Initial moisture content i% w/w basis) 25 60 37 70 30
Final moisture content (% w/w basis) nil 12 3 12 8.5
1200 1200
Air inlet temperature (OF) 450 1300 1200
Air ouitiet temperature (“F) 200/300 2 0 0 / 3 0 0 200/300 200/300 200/300
Method of heating direct direct direct direct direct
oil oil oil oil oil
Heat consumption bBtu/lb water evaporated) 1.6X io3 1.9 x io3 3.1 x io3 7.9~ io3 1.4~ ?03
Air rei5 rcu lation no no no no tl0
Material recirculation yes Yes no yes no
Material of construction MS MS/SS MS MS MS
Fan capacity (std. ft3/min) 18,000 22,000 4300 8500 1500
Installed fan HP 110 180 30 50 10
200 200 - 135
Product exit temperature (OF)
(Courtesy International Combustion Products Ltd.; Williams-Gardner, 1971).