Page 71 - Chemical Process Equipment - Selection and Design
P. 71
3.3. EQUIPMENT CONTROL 43
meters also are available. The flow measurement is transmitted to a
Analysis (composition) controller, transmitter controller which then adjusts the opening of a control valve so as to
maintain the desired condition.
Differential pressure controller, transmitter
FLOW OF SOLIDS
Except for continuous weighing, control of the flow of solids is less
Fllow rate controller, transmitter precise than that of fluids. Several devices used for control of feed
rates are shown schematically in Figure 3.7. They all employ
variable speed drives and are individually calibrated to relate speed
and flow rate. Ordinarily these devices are in effect manually set,
Liquid level controller, transmitter but if the solid material is being fed to a reactor, some property of
the mixture could be used for feed back control. The continuous
belt weigher is capable ordinarily of il% accuracy and even
f0.170 when necessary. For processes such as neutralizations with
Pressure controller, transmitter
lime, addition of the solid to process in slurry form is acceptable.
The slurry is prepared as a batch of definite concentration and
charged with a pump under flow control, often with a diaphragm
00 pump whose stroke can be put under feedback control. For some
Temperature controller, transmitter
applications it is adequate or necessary to feed weighed amounts of
solids to a process on a timed basis.
General symbol for transmitter
FLOW RATIO
Flow ratio control is essential in processes such as fuel-air mixing,
blending, and reactor feed systems. In 2 two-stream process, for
C:ontrol valve example, each stream will have its own controller, but the signal
from the primary controller will go to a ratio control device which
adjusts the set point of the other controller. Figure 3.17(a) is an
I, Signal line, pneumaiic or electrical example. Construction of the ratioing device may be an adjustable
N /
mechanical linkage or may be entirely pneumatic or electronic. In
other two-stream operations, the flow rate of the secondary stream
may be controlled by some property of the combined stream,
temperature in the case of fuel-air systems or composition or some
physical property indicative of the proportions of the two streams.
COMPOSITION
Point of detection
The most common detectors of specific substances are gas
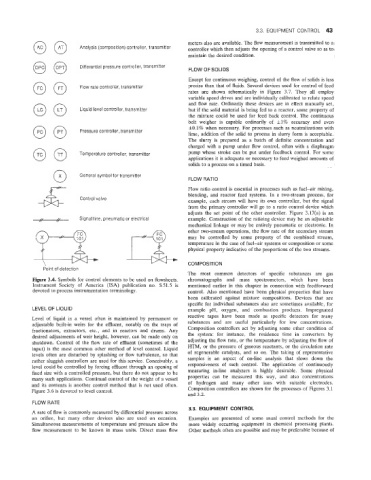
Figure 3.4. Symbols for control elements to be used on flowsheets. chromatographs and mass spectrometers, which have been
Instrument Society of America (ISA) publication no. S51.5 is mentioned earlier in this chapter in connection with feedfonvard
devoted to process instrumentation terminology. control. Also mentioned have been physical properties that have
been calibrated against mixture compositions. Devices that are
specific for individual substances also are sometimes available, for
LEVEL OF LIQUID example pH, oxygen, and combustion products. Impregnated
Level of liquid in a vessel often is maintained by permanent or reactive tapes have been made as specific detectors for wany
adjustable built-in weirs for the effluent, notably on the trays of substances and are useful particularly for low concentrations.
fractionators, extractors, etc., and in reactors and drums. Any Composition controllers act by adjusting some other condition of
desired adjustments of weir height, however, can be made only on the system: for instance, the residence time in converters by
shutdown. Control of the flow rate of effluent (sometimes of the adjusting the flow rate, or the temperature by adjusting the flow of
input) is the most common other method of level control. Liquid HTM, or the pressure of gaseous reactants, or the circulation rate
levels often are disturbed by splashing or flow turbulence, so that of regenerable catalysts, and so on. The taking of representative
rather sluggish controllers are used for this service. Conceivably, a samples is an aspect of on-line analysis that slows down the
level could be controlled by forcing effluent through an opening of responsiveness of such control. The application of continuously
fixed size with a controlled pressure, but there do not appear to be measuring in-line analyzers is highly desirable. Some physical
many such applications. Continual control of the weight of a vessel properties can be measured this way, and also concentrations
and its contents is another control method that is not used often. of hydrogen and many other ions with suitable electrodes.
Figure 3.4 is devoted to level control. Composition controllers are shown for the processes of Figures 3.1
and 3.2.
FLOW RATE
3.3. EQUIPMENT CONTROL
A rate of flow is commonly measured by differential pressure across
an orifice, but many other devices also are used on occasion. Examples are presented of some usual control methods for the
Simultaneous measurements of temperature and pressure allow the more widely occurring equipment in chemical processing plants.
flow measurement to be known in mass units. Direct mass flow Other methods often are possible and may be preferable because of