Page 74 - Chemical Process Equipment - Selection and Design
P. 74
46 PROCESS CONTROL
PF VAPOR
-__-------
(a) =fry+
STM
___
P PF CONDENSATE
steam trap or
liquid level controller
PF VAPOR
(b) + PF CONDENSATE
4 PF CONDENSATE
(C)
accumulator drum
HTM 10-15 FT
PF CONDENSATE
(d) i
~7 trap
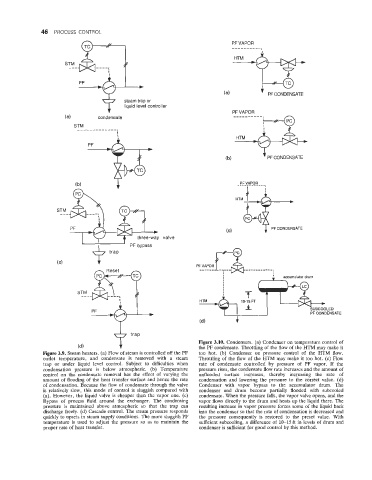
Figure 3.10. Condensers. (a) Condenser on temperature control of
the PF condensate. Throttling of the flow of the HTM may make it
too hot. (b) Condenser on pressure control of the HTM flow.
Throttling of the flow of the HTM may make it too hot. (c) Flow
rate of condensate controlled by pressure of PF vapor. If the
pressure rises, the condensate flow rate increases and the amount of
unflooded surface increases, thereby increasing the rate of
condensation and lowering the pressure to the correct value. (d)
Condenser with vapor bypass to the accumulator drum. The
condenser and drum become partially flooded with subcooled
condensate. When the pressure falls, the vapor valve opens, and the
vapor flows directly to the drum and heats up the liquid there. The
resulting increase in vapor pressure forces some of the liquid back
into the condenser so that the rate of condensation is decreased and
the pressure consequently is restored to the preset value. With
sufficient subcooling, a difference of 10-15 ft in levels of drum and
condenser is sufficient for good control by this method.