Page 142 - Computational Modeling in Biomedical Engineering and Medical Physics
P. 142
Electrical activity of the heart 131
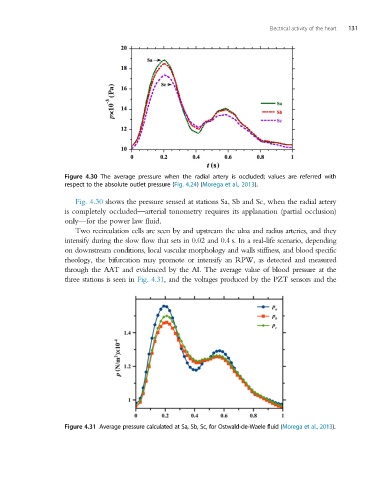
Figure 4.30 The average pressure when the radial artery is occluded; values are referred with
respect to the absolute outlet pressure (Fig. 4.24)(Morega et al., 2013).
Fig. 4.30 shows the pressure sensed at stations Sa, Sb and Sc, when the radial artery
is completely occluded—arterial tonometry requires its applanation (partial occlusion)
only—for the power law fluid.
Two recirculation cells are seen by and upstream the ulna and radius arteries, and they
intensify during the slow flow that sets in 0.02 and 0.4 s. In a real-life scenario, depending
on downstream conditions, local vascular morphology and walls stiffness, and blood specific
rheology, thebifurcation maypromote or intensify an RPW, as detected and measured
through the AAT and evidenced by the AI. The average value of blood pressure at the
three stations is seen in Fig. 4.31, and the voltages produced by the PZT sensors and the
Figure 4.31 AveragepressurecalculatedatSa, Sb, Sc, for Ostwald-de-Waele fluid (Morega et al., 2013).