Page 339 - Computational Statistics Handbook with MATLAB
P. 339
328 Computational Statistics Handbook with MATLAB
0.25
0.2 Class ω Class ω
1
2
0.15
0.1
0.05
0
−6 −4 −2 0 2 4 6 8
Feature − x
IG
FI F U URE G 9. RE 9. 5 5
5
F F II GU RE RE 9. 9. 5
GU
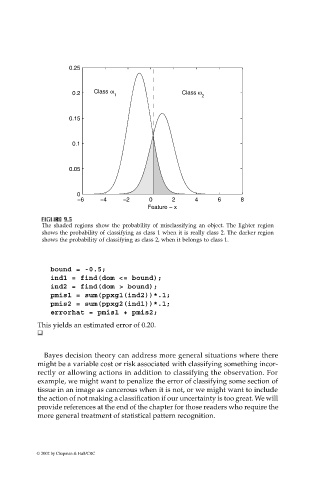
The shaded regions show the probability of misclassifying an object. The lighter region
shows the probability of classifying as class 1 when it is really class 2. The darker region
shows the probability of classifying as class 2, when it belongs to class 1.
bound = -0.5;
ind1 = find(dom <= bound);
ind2 = find(dom > bound);
pmis1 = sum(ppxg1(ind2))*.1;
pmis2 = sum(ppxg2(ind1))*.1;
errorhat = pmis1 + pmis2;
This yields an estimated error of 0.20.
Bayes decision theory can address more general situations where there
might be a variable cost or risk associated with classifying something incor-
rectly or allowing actions in addition to classifying the observation. For
example, we might want to penalize the error of classifying some section of
tissue in an image as cancerous when it is not, or we might want to include
the action of not making a classification if our uncertainty is too great. We will
provide references at the end of the chapter for those readers who require the
more general treatment of statistical pattern recognition.
© 2002 by Chapman & Hall/CRC