Page 199 -
P. 199
168 CHAPTER 5 / INTERNAL MEMORY
Memory
address
register
(MAR)
1/512 A1 1/512 B1 C1 D1 Memory
buffer
9 1/512 1/512
register
E E E E (MBR)
Bit 1 1
9 A2 B2 All chips 512 words by 2
512 bits. 2-terminal cells
A7
2
1/512 B7 C7 D7 7
8
Group E
Chip A
group B
C
enable D 1/512 A8 B8 C8 D8
Select 1
of 4 1/512 1/512
groups
E E E E
Bit 8
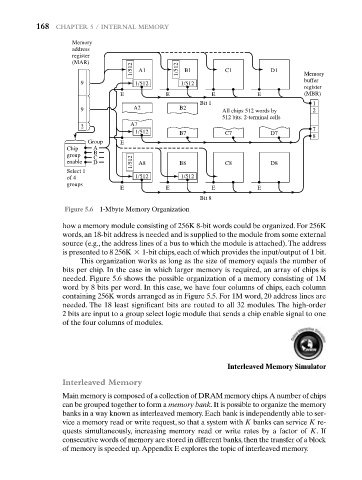
Figure 5.6 1-Mbyte Memory Organization
how a memory module consisting of 256K 8-bit words could be organized. For 256K
words, an 18-bit address is needed and is supplied to the module from some external
source (e.g., the address lines of a bus to which the module is attached).The address
is presented to 8 256K * 1-bit chips, each of which provides the input/output of 1 bit.
This organization works as long as the size of memory equals the number of
bits per chip. In the case in which larger memory is required, an array of chips is
needed. Figure 5.6 shows the possible organization of a memory consisting of 1M
word by 8 bits per word. In this case, we have four columns of chips, each column
containing 256K words arranged as in Figure 5.5. For 1M word, 20 address lines are
needed. The 18 least significant bits are routed to all 32 modules. The high-order
2 bits are input to a group select logic module that sends a chip enable signal to one
of the four columns of modules.
Interleaved Memory Simulator
Interleaved Memory
Main memory is composed of a collection of DRAM memory chips.A number of chips
can be grouped together to form a memory bank.It is possible to organize the memory
banks in a way known as interleaved memory. Each bank is independently able to ser-
vice a memory read or write request, so that a system with K banks can service K re-
quests simultaneously, increasing memory read or write rates by a factor of K.If
consecutive words of memory are stored in different banks,then the transfer of a block
of memory is speeded up.Appendix E explores the topic of interleaved memory.