Page 249 - Control Theory in Biomedical Engineering
P. 249
dexterity sensory clinical fingers sensory material and sensory
available, available, foot by available, no available, interface flexion feedback available,
Commercially Commercially training VR Controlled Commercially abduction/adduction expensive, Very Commercially flexible wrist Passive sensory no Commercially
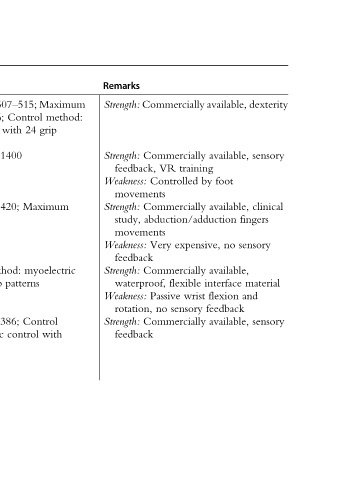
Remarks Strength: Strength: feedback, Weakness: movements Strength: study, movements Weakness: feedback Strength: waterproof, Weakness: rotation, Strength: feedback
Maximum method: grip Maximum myoelectric Control with
507–515; Control 24 with 1400 420; method: patterns 386; control
(g): 136; (N): control (g): (g): 70 (N): grip 23 (g): myoelectric
Weight force Weight Weight force Control with Weight patterns
Description 6; DOFs: grasp myoelectric patterns 6; DOFs: 4; DOFs: grasp 8; DOFs: control 8; DOFs: method: grip 14
of type
WD—cont’d Main WD Myoelectric prosthetic arm Myoelectric prosthetic arm Myoelectric prosthetic arm Myoelectric prosthetic arm Myoelectric prosthetic arm
of
Overview Researcher Ultra Arm, Bionics Hand, 3, 3
1 (2019) Mobius (2019) Michelangelo Hand, Ottobockus (2019) Taska Prosthetics (2019) VINCENT evolution VINCENT evolution (2019)
Table Device, I-Limb LUKE TASKA