Page 245 - Control Theory in Biomedical Engineering
P. 245
robust of clinical no dynamic sensory self- sensory multi- sensory
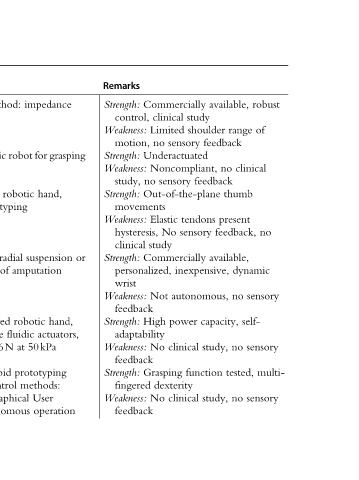
available, range shoulder feedback no feedback thumb present feedback, available, inexpensive, no capacity, no study, tested, function no study,
Commercially study clinical Limited sensory no Underactuated Noncompliant, sensory no Out-of-the-plane tendons Elastic sensory No study Commercially autonomous, Not power High clinical No Grasping dexterity clinical No
Remarks Strength: control, Weakness: motion, Strength: Weakness: study, Strength: movements Weakness: hysteresis, clinical Strength: personalized, wrist Weakness: feedback Strength: adaptability Weakness: feedback Strength: fingered Weakness: feedback
impedance grasping for hand, or suspension amputation hand, robotic actuators, 50kPa prototyping methods: User operation
method: robot prosthetic robotic fingers prototyping trans-radial of level fluidic flexible at 6N of rapid Control Graphical autonomous
Control five rapid trans-radial, Five-fingered small-size force additive manufacturing; control, and
Description 6; DOFs: control Three-fingers tasks 15, DOFs: additive manufacturing For trans-humeral 13, DOFs: 18 maximum 14, DOFs: joystick Interface,
of type exoskeleton Body-powered
WD—cont’d Main WD Assistive Underactuated prosthetic hand Underactuated prosthetic hand prosthetic arm Electrically powered prosthetic hand Electrically powered prosthetic hand
of (2001) (2011)
Overview Researcher Power (2002) al. al. et Hand, Hand al. al.
1 (2020) et e (2010) Victoria (2019) et et
Table Device, Armeo Massa Lalibert Victoria Schulz Bahari