Page 109 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 109
84 C h a p t e r 4
2
1.5
b
1 Fe 3+ Fe(OH) 3
2+
Potential (V vs. SHE) –0.5 0 Cathodic Protection Criterion HFeO 2 –
Fe
0.5
a
–1 Fe(OH) 2
–1.5
Fe
–2
–2 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
pH
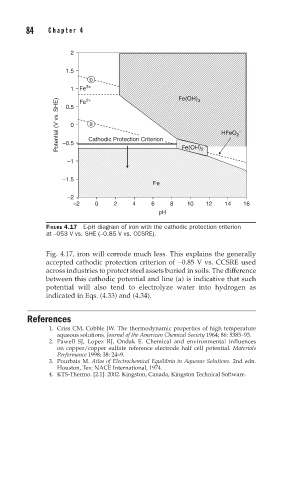
FIGURE 4.17 E-pH diagram of iron with the cathodic protection criterion
at –053 V vs. SHE (–0.85 V vs. CCSRE).
Fig. 4.17, iron will corrode much less. This explains the generally
accepted cathodic protection criterion of −0.85 V vs. CCSRE used
across industries to protect steel assets buried in soils. The difference
between this cathodic potential and line (a) is indicative that such
potential will also tend to electrolyze water into hydrogen as
indicated in Eqs. (4.33) and (4.34).
References
1. Criss CM, Cobble JW. The thermodynamic properties of high temperature
aqueous solutions. Journal of the American Chemical Society 1964; 86: 5385–93.
2. Pawell SJ, Lopez RJ, Ondak E. Chemical and environmental influences
on copper/copper sulfate reference electrode half cell potential. Materials
Performance 1998; 38: 24–9.
3. Pourbaix M. Atlas of Electrochemical Equilibria in Aqueous Solutions. 2nd edn.
Houston, Tex: NACE International, 1974.
4. KTS-Thermo. [2.1]. 2002. Kingston, Canada, Kingston Technical Software.