Page 113 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 113
88 C h a p t e r 5 C o r r o s i o n K i n e t i c s a n d A p p l i c a t i o n s o f E l e c t r o c h e m i s t r y 89
–638 mV Potential Scan Rate
30 mA Current
Pstat
W Ref Aux Off
Gstat
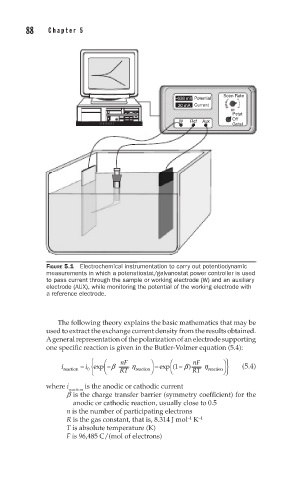
FIGURE 5.1 Electrochemical instrumentation to carry out potentiodynamic
measurements in which a potenstiostat/galvanostat power controller is used
to pass current through the sample or working electrode (W) and an auxiliary
electrode (AUX), while monitoring the potential of the working electrode with
a reference electrode.
The following theory explains the basic mathematics that may be
used to extract the exchange current density from the results obtained.
A general representation of the polarization of an electrode supporting
one specific reaction is given in the Butler-Volmer equation (5.4):
nF nF
i reaction = i exp −b h reaction − exp (1− b ) h reaction (5.4)
1
0
RT RT
where i reaction is the anodic or cathodic current
b is the charge transfer barrier (symmetry coefficient) for the
anodic or cathodic reaction, usually close to 0.5
n is the number of participating electrons
−1
R is the gas constant, that is, 8.314 J mol K −1
T is absolute temperature (K)
F is 96,485 C/(mol of electrons)