Page 134 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 134
108 C h a p t e r 5 C o r r o s i o n K i n e t i c s a n d A p p l i c a t i o n s o f E l e c t r o c h e m i s t r y 109
1600
1200
Potential (mV vs. SCE) 800 0
400
–400
–800
–6 –5.5 –5 –4.5 –4 –3.5 –3 –2.5 –2 –1.5
Log Current (A)
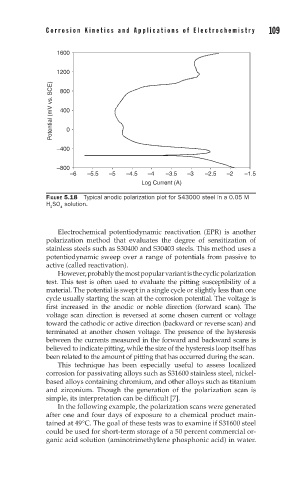
FIGURE 5.18 Typical anodic polarization plot for S43000 steel in a 0.05 M
H SO solution.
2 4
Electrochemical potentiodynamic reactivation (EPR) is another
polarization method that evaluates the degree of sensitization of
stainless steels such as S30400 and S30403 steels. This method uses a
potentiodynamic sweep over a range of potentials from passive to
active (called reactivation).
However, probably the most popular variant is the cyclic polarization
test. This test is often used to evaluate the pitting susceptibility of a
material. The potential is swept in a single cycle or slightly less than one
cycle usually starting the scan at the corrosion potential. The voltage is
first increased in the anodic or noble direction (forward scan). The
voltage scan direction is reversed at some chosen current or voltage
toward the cathodic or active direction (backward or reverse scan) and
terminated at another chosen voltage. The presence of the hysteresis
between the currents measured in the forward and backward scans is
believed to indicate pitting, while the size of the hysteresis loop itself has
been related to the amount of pitting that has occurred during the scan.
This technique has been especially useful to assess localized
corrosion for passivating alloys such as S31600 stainless steel, nickel-
based alloys containing chromium, and other alloys such as titanium
and zirconium. Though the generation of the polarization scan is
simple, its interpretation can be difficult [7].
In the following example, the polarization scans were generated
after one and four days of exposure to a chemical product main-
tained at 49°C. The goal of these tests was to examine if S31600 steel
could be used for short-term storage of a 50 percent commercial or-
ganic acid solution (aminotrimethylene phosphonic acid) in water.