Page 735 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 735
688 C h a p t e r 1 5 H i g h - Te m p e r a t u r e C o r r o s i o n 689
The vapor aluminum-diffused surface layer is hard and brittle, but
the bulk substrate retains the properties of conventional steels.
Extensive testing of alloys has shown that many alloys establish
parabolic time dependence after a minimum time of 1000 hours in air
at temperatures above 900°C. If the surface corrosion product (scale) is
removed or cracked so that the underlying metal is exposed to the gas,
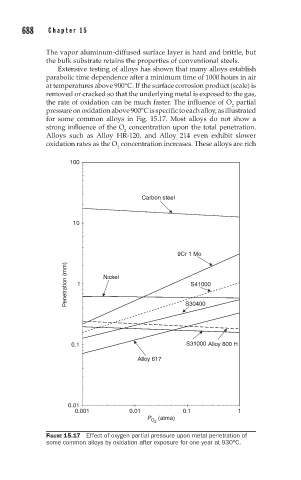
the rate of oxidation can be much faster. The influence of O partial
2
pressure on oxidation above 900°C is specific to each alloy, as illustrated
for some common alloys in Fig. 15.17. Most alloys do not show a
strong influence of the O concentration upon the total penetration.
2
Alloys such as Alloy HR-120, and Alloy 214 even exhibit slower
oxidation rates as the O concentration increases. These alloys are rich
2
100
Carbon steel
10
9Cr 1 Mo
Penetration (mm) 1 Nickel S30400
S41000
0.1 S31000 Alloy 800 H
Alloy 617
0.01
0.001 0.01 0.1 1
(atma)
P O
2
FIGURE 15.17 Effect of oxygen partial pressure upon metal penetration of
some common alloys by oxidation after exposure for one year at 930°C.