Page 98 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 98
72 C h a p t e r 4 C o r r o s i o n T h e r m o d y n a m i c s 73
for pH measurements. Modern pH meters have temperature com-
pensation (either automatic or manual) to correct for variations in
slope caused by changes in temperature.
Buffers: These solutions of known pH value allow the user to cali-
brate the system to read accurate measurements.
4.7.1 Glass Electrodes
A glass electrode is a potentiometric sensor made from glass of a
specific composition. All glass pH electrodes have extremely high
electric resistance from 50 to 500 MΩ. There are different types of pH
glass electrodes. Some of them have improved characteristics for
working in very alkaline or acidic medium. But almost all electrodes
can operate in the 1 to 12 pH range.
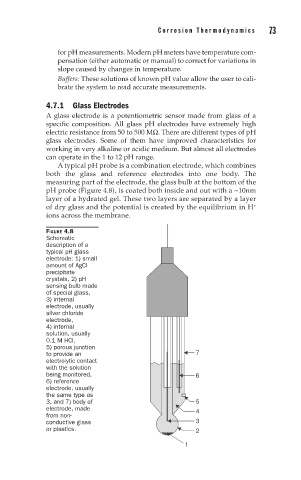
A typical pH probe is a combination electrode, which combines
both the glass and reference electrodes into one body. The
measuring part of the electrode, the glass bulb at the bottom of the
pH probe (Figure 4.8), is coated both inside and out with a ~10nm
layer of a hydrated gel. These two layers are separated by a layer
+
of dry glass and the potential is created by the equilibrium in H
ions across the membrane.
FIGURE 4.8
Schematic
description of a
typical pH glass
electrode: 1) small
amount of AgCl
precipitate
crystals, 2) pH
sensing bulb made
of special glass,
3) internal
electrode, usually
silver chloride
electrode,
4) internal
solution, usually
0.1 M HCl,
5) porous junction
to provide an 7
electrolytic contact
with the solution
being monitored, 6
6) reference
electrode, usually
the same type as
3, and 7) body of 5
electrode, made 4
from non-
conductive glass 3
or plastics. 2
1