Page 276 - DSP Integrated Circuits
P. 276
6.9 Algorithm Transformations 261
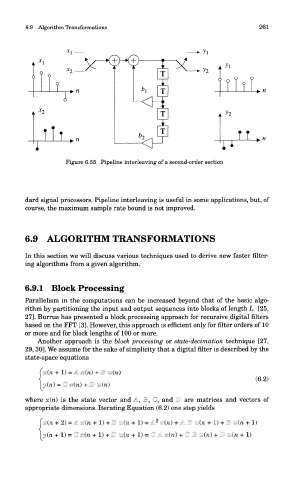
Figure 6.55 Pipeline interleaving of a second-order section
dard signal processors. Pipeline interleaving is useful in some applications, but, of
course, the maximum sample rate bound is not improved.
6.9 ALGORITHM TRANSFORMATIONS
In this section we will discuss various techniques used to derive new faster filter-
ing algorithms from a given algorithm.
6.9.1 Block Processing
Parallelism in the computations can be increased beyond that of the basic algo-
rithm by partitioning the input and output sequences into blocks of length L [25,
271. Burrus has presented a block processing approach for recursive digital filters
based on the FFT [3]. However, this approach is efficient only for filter orders of 10
or more and for block lengths of 100 or more.
Another approach is the block processing or state-decimation technique [27,
29, 30]. We assume for the sake of simplicity that a digital filter is described by the
state-space equations
where x(n) is the state vector and A, B, C, and D are matrices and vectors of
appropriate dimensions. Iterating Equation (6.2) one step yields