Page 411 - DSP Integrated Circuits
P. 411
396 Chapter 9 Synthesis of DSP Architectures
Cathedral I is based on about 20 bit-
serial building blocks. Due to the bit-serial
processing, only a small number of memory
and logic blocks such as flip-flops, shift regis-
ters, adders, and sign-extenders are needed.
Sign-extenders, which will be further dis-
cussed in Chapter 11, are special circuits
required to perform multiplication with
signed numbers. These blocks can be designed
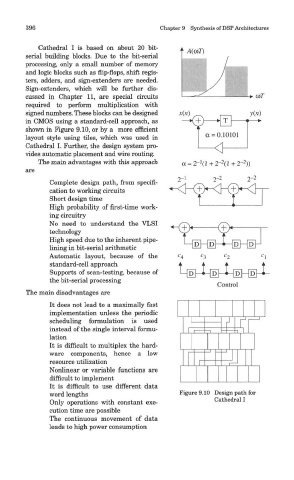
in CMOS using a standard-cell approach, as
shown in Figure 9.10, or by a more efficient
layout style using tiles, which was used in
Cathedral I. Further, the design system pro-
vides automatic placement and wire routing.
The main advantages with this approach
are
Complete design path, from specifi-
cation to working circuits
Short design time
High probability of first-time work-
ing circuitry
No need to understand the VLSI
technology
High speed due to the inherent pipe-
lining in bit-serial arithmetic
Automatic layout, because of the
standard-cell approach
Supports of scan-testing, because of
the bit-serial processing
The main disadvantages are
It does not lead to a maximally fast
implementation unless the periodic
scheduling formulation is used
instead of the single interval formu-
lation
It is difficult to multiplex the hard-
ware components, hence a low
resource utilization
Nonlinear or variable functions are
difficult to implement
It is difficult to use different data
word lengths Figure 9.10 Design path for
Cathedral I
Only operations with constant exe-
cution time are possible
The continuous movement of data
leads to high power consumption