Page 527 - DSP Integrated Circuits
P. 527
512 Chapter 11 Processing Elements
where the control signal x sig n.i)H is zero at all times except when the sign-bit
arrives.
«1 « 2 A/S
F k
X\ X 2 X 3
0 0 0 -01 -o 2 -03 0 0 A
0 0 1 -01 -o 2 + 03 0 1 A
0 1 0 -01 + 02 -03 1 0 A
0 1 1 -01 + 02 + 03 1 1 A
1 0 0 +01 -o 2 -03 1 1 S
1 0 1 +01 -o 2 + 03 1 0 S
1 1 0 +01 + 02 -03 0 1 s
1 1 1 +01 + 02 + 03 0 0 s
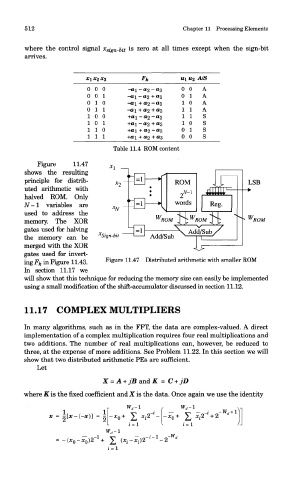
Table 11.4 ROM content
Figure 11.47
shows the resulting
principle for distrib-
uted arithmetic with
halved ROM. Only
N-l variables are
used to address the
memory. The XOR ROM
gates used for halving
the memory can be ^Sign-bit
merged with the XOR
gates used for invert-
ing F& in Figure 11.43. Figure 11.47 Distributed arithmetic with smaller ROM
In section 11.17 we
will show that this technique for reducing the memory size can easily be implemented
using a small modification of the shift-accumulator discussed in section 11.12.
11.17 COMPLEX MULTIPLIERS
In many algorithms, such as in the FFT, the data are complex-valued. A direct
implementation of a complex multiplication requires four real multiplications and
two additions. The number of real multiplications can, however, be reduced to
three, at the expense of more additions. See Problem 11.22. In this section we will
show that two distributed arithmetic PEs are sufficient.
Let
X = A + JB and K = C + jD
where K is the fixed coefficient and X is the data. Once again we use the identity
.-& <-*>] = 2
,-i-i_ 2-^
; = i