Page 249 - Defrosting for Air Source Heat Pump
P. 249
244 Defrosting for Air Source Heat Pump
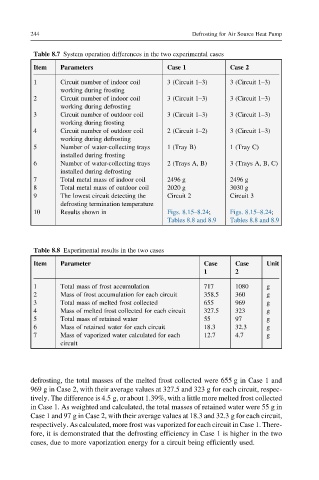
Table 8.7 System operation differences in the two experimental cases
Item Parameters Case 1 Case 2
1 Circuit number of indoor coil 3 (Circuit 1–3) 3 (Circuit 1–3)
working during frosting
2 Circuit number of indoor coil 3 (Circuit 1–3) 3 (Circuit 1–3)
working during defrosting
3 Circuit number of outdoor coil 3 (Circuit 1–3) 3 (Circuit 1–3)
working during frosting
4 Circuit number of outdoor coil 2 (Circuit 1–2) 3 (Circuit 1–3)
working during defrosting
5 Number of water-collecting trays 1 (Tray B) 1 (Tray C)
installed during frosting
6 Number of water-collecting trays 2 (Trays A, B) 3 (Trays A, B, C)
installed during defrosting
7 Total metal mass of indoor coil 2496 g 2496 g
8 Total metal mass of outdoor coil 2020 g 3030 g
9 The lowest circuit detecting the Circuit 2 Circuit 3
defrosting termination temperature
10 Results shown in Figs. 8.15–8.24; Figs. 8.15–8.24;
Tables 8.8 and 8.9 Tables 8.8 and 8.9
Table 8.8 Experimental results in the two cases
Item Parameter Case Case Unit
1 2
1 Total mass of frost accumulation 717 1080 g
2 Mass of frost accumulation for each circuit 358.5 360 g
3 Total mass of melted frost collected 655 969 g
4 Mass of melted frost collected for each circuit 327.5 323 g
5 Total mass of retained water 55 97 g
6 Mass of retained water for each circuit 18.3 32.3 g
7 Mass of vaporized water calculated for each 12.7 4.7 g
circuit
defrosting, the total masses of the melted frost collected were 655 g in Case 1 and
969 g in Case 2, with their average values at 327.5 and 323 g for each circuit, respec-
tively. The difference is 4.5 g, or about 1.39%, with a little more melted frost collected
in Case 1. As weighted and calculated, the total masses of retained water were 55 g in
Case 1 and 97 g in Case 2, with their average values at 18.3 and 32.3 g for each circuit,
respectively. As calculated, more frost was vaporized for each circuit in Case 1. There-
fore, it is demonstrated that the defrosting efficiency in Case 1 is higher in the two
cases, due to more vaporization energy for a circuit being efficiently used.