Page 286 - Design of Simple and Robust Process Plants
P. 286
272 Chapter 7 Optimization of an Integrated Complex of Process Plants
The above data are to be used for a cost±benefit analysis of capacity loss and opera-
tional losses versus investment to obtain an optimal process. The process alterna-
tives to be evaluated are process reliability, as well as storage capacity.
7.6.4
A Chain of Production Processes
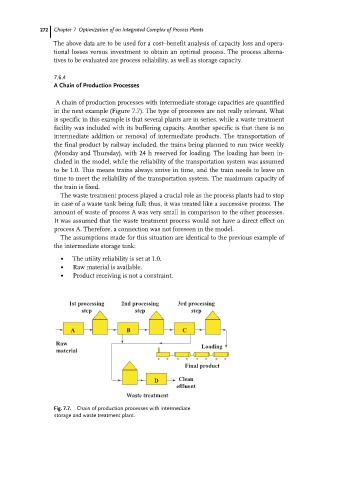
A chain of production processes with intermediate storage capacities are quantified
in the next example (Figure 7.7). The type of processes are not really relevant. What
is specific in this example is that several plants are in series, while a waste treatment
facility was included with its buffering capacity. Another specific is that there is no
intermediate addition or removal of intermediate products. The transportation of
the final product by railway included, the trains being planned to run twice weekly
(Monday and Thursday), with 24 h reserved for loading. The loading has been in-
cluded in the model, while the reliability of the transportation system was assumed
to be 1.0. This means trains always arrive in time, and the train needs to leave on
time to meet the reliability of the transportation system. The maximum capacity of
the train is fixed.
The waste treatment process played a crucial role as the process plants had to stop
in case of a waste tank being full; thus, it was treated like a successive process. The
amount of waste of process A was very small in comparison to the other processes.
It was assumed that the waste treatment process would not have a direct effect on
process A. Therefore, a connection was not foreseen in the model.
The assumptions made for this situation are identical to the previous example of
the intermediate storage tank:
. The utility reliability is set at 1.0.
. Raw material is available.
. Product receiving is not a constraint.
1st processing 2nd processing 3rd processing
step step step
A B C
Raw Loading
material
Final product
D Clean
effluent
Waste treatment
Fig. 7.7. Chain of production processes with intermediate
storage and waste treatment plant.