Page 133 - Electric Drives and Electromechanical Systems
P. 133
126 Electric Drives and Electromechanical Systems
of complete pitches is counted to determine the total distance move. The pitch of a
metric linear Inductosyn is such that a resolution of 5 10 6 m can to be achieved.
Rotary Inductosyns are supplied with pitch counts in the range 32e2048 per revolution,
with achievable accuracies to 0.5 s of arc.
4.3.5 Optical position sensors
Optically based encoders are widely used for position measurements in robots and
machine tools. They can take one of three forms: absolute, semi-absolute, and incre-
mental. Each of these types of encoder consists of three elements: an optical receiver, a
light source, and a code wheel. The receiver is normally a phototransistor or diode which
responds to the light intensity which is received. As discussed earlier, the light source can
either be a solid-state light-emitting diode or a filament bulb. The difference between the
types of encoders is characterised by the information contained on the code wheel and
by how it is interpreted by an external control system.
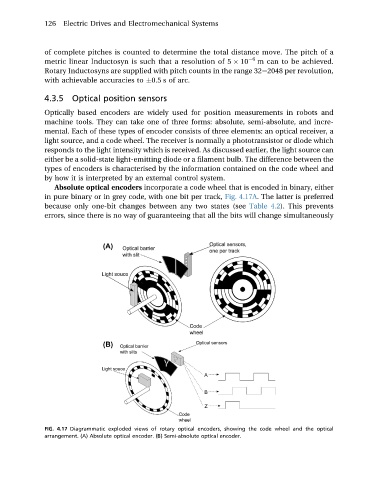
Absolute optical encoders incorporate a code wheel that is encoded in binary, either
in pure binary or in grey code, with one bit per track, Fig. 4.17A. The latter is preferred
because only one-bit changes between any two states (see Table 4.2). This prevents
errors, since there is no way of guaranteeing that all the bits will change simultaneously
FIG. 4.17 Diagrammatic exploded views of rotary optical encoders, showing the code wheel and the optical
arrangement. (A) Absolute optical encoder. (B) Semi-absolute optical encoder.