Page 161 - Electric Drives and Electromechanical Systems
P. 161
154 Electric Drives and Electromechanical Systems
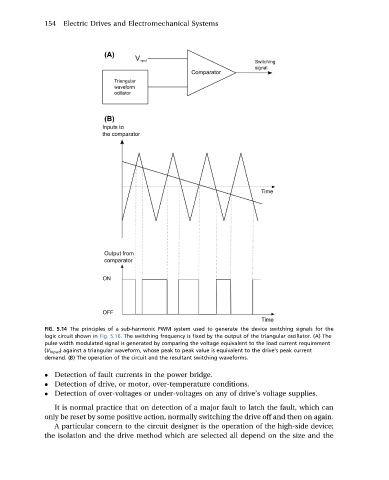
FIG. 5.14 The principles of a sub-harmonic PWM system used to generate the device switching signals for the
logic circuit shown in Fig. 5.16. The switching frequency is fixed by the output of the triangular oscillator. (A) The
pulse width modulated signal is generated by comparing the voltage equivalent to the load current requirement
(V input ) against a triangular waveform, whose peak to peak value is equivalent to the drive’s peak current
demand. (B) The operation of the circuit and the resultant switching waveforms.
Detection of fault currents in the power bridge.
Detection of drive, or motor, over-temperature conditions.
Detection of over-voltages or under-voltages on any of drive’s voltage supplies.
It is normal practice that on detection of a major fault to latch the fault, which can
only be reset by some positive action, normally switching the drive off and then on again.
A particular concern to the circuit designer is the operation of the high-side device;
the isolation and the drive method which are selected all depend on the size and the