Page 165 - Electric Drives and Electromechanical Systems
P. 165
158 Electric Drives and Electromechanical Systems
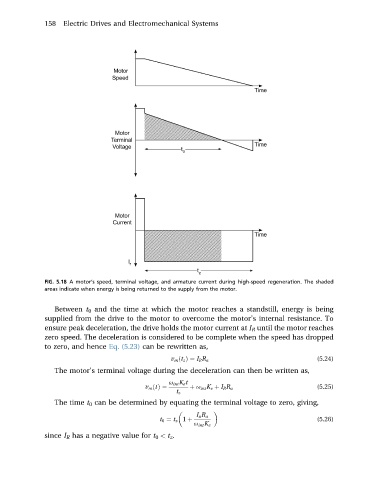
FIG. 5.18 A motor’s speed, terminal voltage, and armature current during high-speed regeneration. The shaded
areas indicate when energy is being returned to the supply from the motor.
Between t 0 and the time at which the motor reaches a standstill, energy is being
supplied from the drive to the motor to overcome the motor’s internal resistance. To
ensure peak deceleration, the drive holds the motor current at I R until the motor reaches
zero speed. The deceleration is considered to be complete when the speed has dropped
to zero, and hence Eq. (5.23) can be rewritten as,
(5.24)
v m ðt z Þ¼ I R R a
The motor’s terminal voltage during the deceleration can then be written as,
u int K e t
v m ðtÞ¼ þ u int K e þ I R R a (5.25)
t z
The time t 0 can be determined by equating the terminal voltage to zero, giving,
I a R a
t 0 ¼ t z 1 þ (5.26)
u int K e
since I R has a negative value for t 0 < t z .