Page 88 - Electric Drives and Electromechanical Systems
P. 88
Chapter 3 Power transmission and sizing 81
harmonic drives have a high torque capability; in addition, the backlash is very small,
being typically less than 30 s of arc.
In practice, any two of the three components that make up the gearbox can be used as
the input to, and the output from, the gearbox, giving the designer considerable flexi-
bility. The robotic hand shown in Fig. 1.10 incorporated three harmonic gearboxes of a
pancake design.
3.1.4 Cycloid gearbox
The cycloid gearbox is of a co-axial design and offers high reduction ratios in a single
stage and is noted for its high stiffness and low backlash. The gearbox is suitable for
heavy duty applications, since it has a very high shock load capability of up to 500%.
Commercially cycloid gearboxes are available in a range of sizes with ratios between 6:1
and 120:1 and with a power transmission capability of up to approximately 100 kW.
The gearbox design, which is both highly reliable and efficient, undertakes the speed
conversion by using rolling actions, with the power being transmitted by cycloid discs
driven by an eccentric bearing.
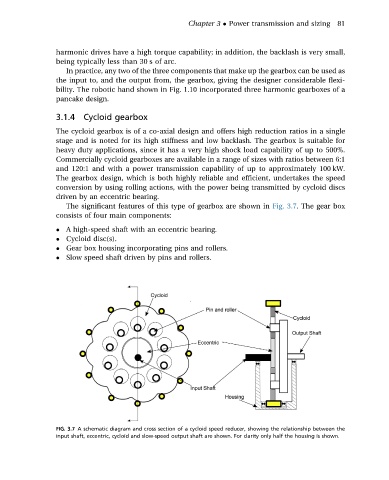
The significant features of this type of gearbox are shown in Fig. 3.7. The gear box
consists of four main components:
A high-speed shaft with an eccentric bearing.
Cycloid disc(s).
Gear box housing incorporating pins and rollers.
Slow speed shaft driven by pins and rollers.
FIG. 3.7 A schematic diagram and cross section of a cycloid speed reducer, showing the relationship between the
input shaft, eccentric, cycloid and slow-speed output shaft are shown. For clarity only half the housing is shown.