Page 22 - Electrical Equipment Handbook _ Troubleshooting and Maintenance
P. 22
FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRIC SYSTEMS
FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRIC SYSTEMS 1.21
The unit of this power is voltamperes (VA) or megavoltamperes (MVA). This power
includes the combined effect of the real power and the reactive power. All electrical
equipment such as transformers, motors, and generators are rated by their apparent
power. This is so because the apparent power specifies the total power (real and reac-
tive) requirement of equipment.
THREE-PHASE SYSTEMS
Most of the transmission, distribution, and energy conversion systems having an apparent
power higher than 10 kVA use three-phase circuits. The reason for this is that the power
density (the ratio of power to weight) of a device is higher when it is a three-phase rather
than a single-phase design. For example, the weight of a three-phase motor is lower than
the weight of a single-phase motor having the same rating. The voltages of a three-phase
system are normally given by
v V sin t
a′a m
v b′b V sin ( t 120°)
m
v V sin ( t 240°)
c′c m
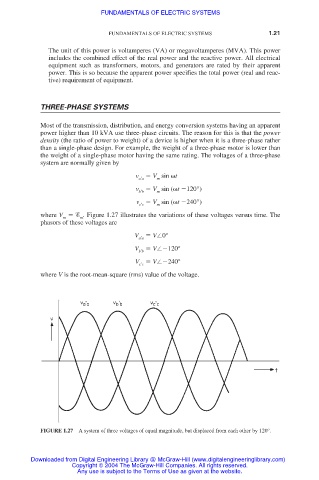
where V . Figure 1.27 illustrates the variations of these voltages versus time. The
m m
phasors of these voltages are
V a′a V 0°
V V 120°
b′b
V V 240°
c′c
where V is the root-mean-square (rms) value of the voltage.
FIGURE 1.27 A system of three voltages of equal magnitude, but displaced from each other by 120°.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.