Page 18 - Electrical Equipment Handbook _ Troubleshooting and Maintenance
P. 18
FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRIC SYSTEMS
FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRIC SYSTEMS 1.17
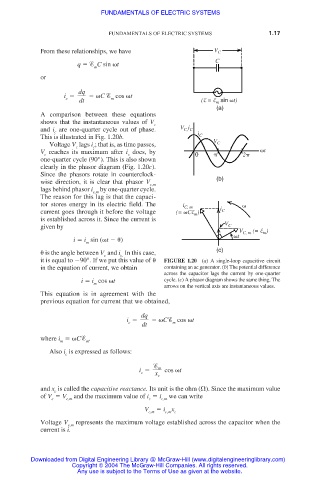
From these relationships, we have V C
C
q C sin t
m
or
dq
i C cos t
c dt m (E = E m sin t)
(a)
A comparison between these equations
shows that the instantaneous values of V
c
i
and i are one-quarter cycle out of phase. V C, C i
c
This is illustrated in Fig. 1.20b. C V
Voltage V lags i ; that is, as time passes, C
c
c
V reaches its maximum after i does, by t
c c 0 2
one-quarter cycle (90°). This is also shown
clearly in the phasor diagram (Fig. 1.20c).
Since the phasors rotate in counterclock-
wise direction, it is clear that phasor V (b)
c,m
lags behind phasor i by one-quarter cycle.
c,m
The reason for this lag is that the capaci-
tor stores energy in its electric field. The i C, m i
current goes through it before the voltage (= CE ) C
m
is established across it. Since the current is
V
given by C
V C, m (= E )
m
t
i i sin ( t )
m
(c)
is the angle between V and i In this case,
c
c.
it is equal to 90°. If we put this value of FIGURE 1.20 (a) A single-loop capacitive circuit
in the equation of current, we obtain containing an ac generator. (b) The potential difference
across the capacitor lags the current by one-quarter
i i cos t cycle. (c) A phasor diagram shows the same thing. The
m
arrows on the vertical axis are instantaneous values.
This equation is in agreement with the
previous equation for current that we obtained,
dq
i C cos t
m
c
dt
where i C .
m
m
Also i is expressed as follows:
c
m
i cos t
c x c
and x is called the capacitive reactance. Its unit is the ohm ( ). Since the maximum value
c
of V V c,m and the maximum value of i i c,m we can write
c
c
V i x
c,m c,m c
Voltage V represents the maximum voltage established across the capacitor when the
c,m
current is i.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.