Page 210 - Electrical Safety of Low Voltage Systems
P. 210
Earth Electrodes, Protective Conductors 193
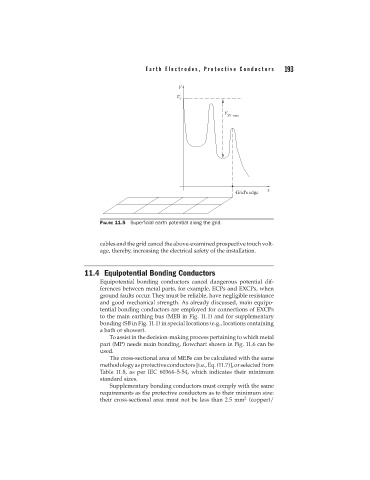
FIGURE 11.5 Superficial earth potential along the grid.
cables and the grid cancel the above-examined prospective touch volt-
age, thereby, increasing the electrical safety of the installation.
11.4 Equipotential Bonding Conductors
Equipotential bonding conductors cancel dangerous potential dif-
ferences between metal parts, for example, ECPs and EXCPs, when
ground faults occur. They must be reliable, have negligible resistance
and good mechanical strength. As already discussed, main equipo-
tential bonding conductors are employed for connections of EXCPs
to the main earthing bus (MEB in Fig. 11.1) and for supplementary
bonding (SB in Fig. 11.1) in special locations (e.g., locations containing
a bath or shower).
To assist in the decision-making process pertaining to which metal
part (MP) needs main bonding, flowchart shown in Fig. 11.6 can be
used.
The cross-sectional area of MEBs can be calculated with the same
methodologyasprotectiveconductors[i.e.,Eq.(11.7)],orselectedfrom
Table 11.8, as per IEC 60364–5-54, which indicates their minimum
standard sizes.
Supplementary bonding conductors must comply with the same
requirements as the protective conductors as to their minimum size:
2
their cross-sectional area must not be less than 2.5 mm (copper)/