Page 199 - Electrical Properties of Materials
P. 199
Metal–insulator–semiconductor junctions 181
Vacuum
) a ( ) b ( ) c (
level
M I S
log N
e
Conduction
band
N E
en F
eU
0
+ – 0 x Valence
band
U
0
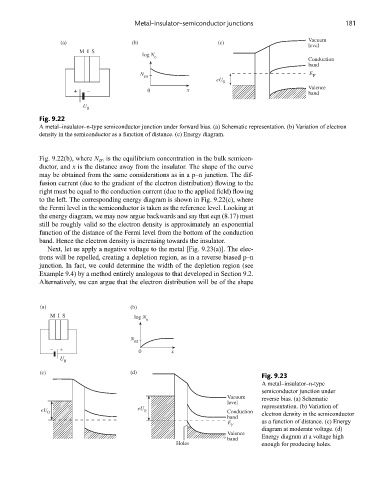
Fig. 9.22
A metal–insulator–n-type semiconductor junction under forward bias. (a) Schematic representation. (b) Variation of electron
density in the semiconductor as a function of distance. (c) Energy diagram.
Fig. 9.22(b), where N en is the equilibrium concentration in the bulk semicon-
ductor, and x is the distance away from the insulator. The shape of the curve
may be obtained from the same considerations as in a p–n junction. The dif-
fusion current (due to the gradient of the electron distribution) flowing to the
right must be equal to the conduction current (due to the applied field) flowing
to the left. The corresponding energy diagram is shown in Fig. 9.22(c), where
the Fermi level in the semiconductor is taken as the reference level. Looking at
the energy diagram, we may now argue backwards and say that eqn (8.17) must
still be roughly valid so the electron density is approximately an exponential
function of the distance of the Fermi level from the bottom of the conduction
band. Hence the electron density is increasing towards the insulator.
Next, let us apply a negative voltage to the metal [Fig. 9.23(a)]. The elec-
trons will be repelled, creating a depletion region, as in a reverse biased p–n
junction. In fact, we could determine the width of the depletion region (see
Example 9.4) by a method entirely analogous to that developed in Section 9.2.
Alternatively, we can argue that the electron distribution will be of the shape
(a) (b)
M I S log N
e
N
en
– + 0 x
U
0
(c) (d)
Fig. 9.23
A metal–insulator–n-type
semiconductor junction under
Vacuum reverse bias. (a) Schematic
level
eU eU 0 representation. (b) Variation of
0 Conduction electron density in the semiconductor
band
E as a function of distance. (c) Energy
F
diagram at moderate voltage. (d)
Valence
band Energy diagram at a voltage high
Holes enough for producing holes.