Page 262 - Electromechanical Devices and Components Illustrated Sourcebook
P. 262
224 Electromechanical Devices & Components Illustrated Sourcebook
When working with electromechnical devices, it is imperative
Magnetized
that the technician be able to gauge certain aspects of the elec- Upholstery Needle
trical power and the signals being utilized by the equipment. Water
This gauging may be as simple as connecting a light bulb to
Cork
verify power or it may require a highly sensitive vacuum tube
voltmeter to monitor extremely low voltages. Similarly, a sig- Bowl
nal may be verified with a simple loudspeaker or it may
require the sophisticated display of an oscilloscope. In any
case, a preliminary understanding of meters and their uses is
extremely valuable information to have under your belt.
Figure 13-2 Bench Built Compass
Compass
Let’s start by examining one of the most basic electromag-
netic instruments, the compass. Figure 13-1 shows a typical
Fixed Coil
commercial compass such as may be found in any sports and
outdoor store. This instrument is made by mounting a magne-
Coil Form
tized needle onto a precision pivot. The pivot allows the needle
to freely align with the magnetic field of the earth. In doing
so, the North Pole of the needle will always point toward the Compass
magnetic North Pole of the earth. The pivot is mounted in the
center of a graduated face, which, in turn, is placed in the bot- Support Post
tom a nonferrous case. The case is typically sealed with a glass
window that prevents the needle from coming off the pivot
Terminal Leveling Foot
when the instrument is transported in a pack or pocket.
Base
Case
Pivot N Figure 13-3 Fixed Coil Galvanometer
N
W E
S to the needle. When an electrical signal was applied to the
Magnetized
Indicator coil, the compass needle deflected. These instruments could
S Face be made to detect extremely low signal levels. Figure 13-3
shows an early laboratory galvanometer.
Figure 13-1 Magnetic Compass Building a fixed coil galvanometer can be accomplished by
winding a coil around a piece of 6-inch polyvinyl chloride
(PVC) pipe, as shown in Figure 13-4. The coil is mounted to
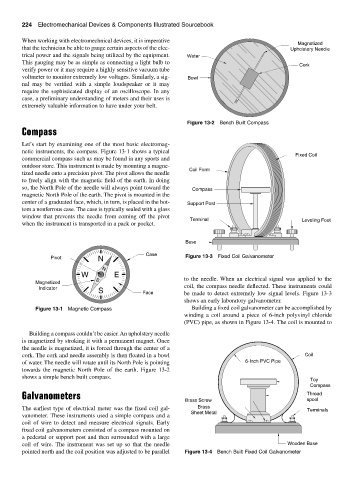
Building a compass couldn’t be easier. An upholstery needle
is magnetized by stroking it with a permanent magnet. Once
the needle is magnetized, it is forced through the center of a
cork. The cork and needle assembly is then floated in a bowl Coil
of water. The needle will rotate until its North Pole is pointing 6-Inch PVC Pipe
towards the magnetic North Pole of the earth. Figure 13-2
shows a simple bench built compass.
Toy
Compass
Galvanometers Thread
Brass Screw spool
The earliest type of electrical meter was the fixed coil gal- Brass Terminals
Sheet Metal
vanometer. These instruments used a simple compass and a
coil of wire to detect and measure electrical signals. Early
fixed coil galvanometers consisted of a compass mounted on
a pedestal or support post and then surrounded with a large
coil of wire. The instrument was set up so that the needle Wooden Base
pointed north and the coil position was adjusted to be parallel Figure 13-4 Bench Built Fixed Coil Galvanometer