Page 263 - Electromechanical Devices and Components Illustrated Sourcebook
P. 263
Chapter 13 Meters 225
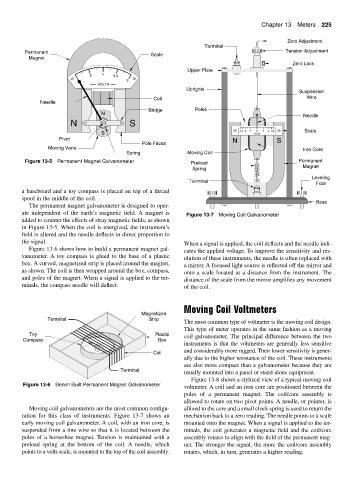
Zero Adjustment
Terminal
Permanent Scale Tension Adjustment
Magnet
Zero Lock
Upper Plate
.5 1 1.5
2
VOLTS
Uprights
Suspension
Coil Wire
Needle
Bridge Poles
N
Needle
N S
4 3 2 1 0 1 2 3 4 Scale
S VOLTS
Pivot N S
Pole Faces
Moving Vane Iron Core
Spring Moving Coil
Figure 13-5 Permanent Magnet Galvanometer Preload Permanent
Spring Magnet
Leveling
Terminal Foot
a baseboard and a toy compass is placed on top of a thread
spool in the middle of the coil.
Base
The permanent magnet galvanometer is designed to oper-
ate independent of the earth’s magnetic field. A magnet is Figure 13-7 Moving Coil Galvanometer
added to counter the effects of stray magnetic fields, as shown
in Figure 13-5. When the coil is energized, the instrument’s
field is altered and the needle deflects in direct proportion to
the signal.
When a signal is applied, the coil deflects and the needle indi-
Figure 13-6 shows how to build a permanent magnet gal-
cates the applied voltage. To improve the sensitivity and res-
vanometer. A toy compass is glued to the base of a plastic
olution of these instruments, the needle is often replaced with
box. A curved, magnetized strip is placed around the magnet,
a mirror. A focused light source is reflected off the mirror and
as shown. The coil is then wrapped around the box, compass,
onto a scale located at a distance from the instrument. The
and poles of the magnet. When a signal is applied to the ter-
distance of the scale from the mirror amplifies any movement
minals, the compass needle will deflect.
of the coil.
Moving Coil Voltmeters
Magnetized
Terminal Strip
The most common type of voltmeter is the moving coil design.
This type of meter operates in the same fashion as a moving
Toy Plastic coil galvanometer. The principal difference between the two
Compass Box
instruments is that the voltmeters are generally less sensitive
and considerably more rugged. Their lower sensitivity is gener-
Coil
ally due to the higher resistance of the coil. These instruments
are also more compact than a galvanometer because they are
Terminal
usually mounted into a panel or stand-alone equipment.
Figure 13-8 shows a stylized view of a typical moving coil
Figure 13-6 Bench Built Permanent Magnet Galvanometer
voltmeter. A coil and an iron core are positioned between the
poles of a permanent magnet. The coil/core assembly is
allowed to rotate on two pivot points. A needle, or pointer, is
Moving coil galvanometers are the most common configu- affixed to the core and a small clock spring is used to return the
ration for this class of instruments. Figure 13-7 shows an mechanism back to a zero reading. The needle points to a scale
early moving coil galvanometer. A coil, with an iron core, is mounted onto the magnet. When a signal is applied to the ter-
suspended from a fine wire so that it is located between the minals, the coil generates a magnetic field and the coil/core
poles of a horseshoe magnet. Tension is maintained with a assembly rotates to align with the field of the permanent mag-
preload spring at the bottom of the coil. A needle, which net. The stronger the signal, the more the coil/core assembly
points to a volts scale, is mounted to the top of the coil assembly. rotates, which, in turn, generates a higher reading.