Page 200 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioTechnology
P. 200
P1: GTV/MBR P2: GSS Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN011L-523 August 10, 2001 11:17
320 Optical Fiber Techniques for Medical Applications
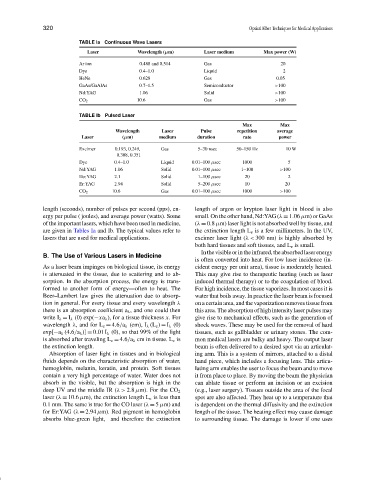
TABLE Ia Continuous Wave Lasers
Laser Wavelength (µm) Laser medium Max power (W)
Ar ion 0.488 and 0.514 Gas 20
Dye 0.4–1.0 Liquid 2
HeNe 0.628 Gas 0.05
GaAs/GaAlAs 0.7–1.5 Semiconductor >100
Nd:YAG 1.06 Solid >100
CO 2 10.6 Gas >100
TABLE Ib Pulsed Laser
Max Max
Wavelength Laser Pulse repetition average
Laser (µm) medium duration rate power
Excimer 0.193, 0.249, Gas 5–30 nsec 50–150 Hz 10 W
0.308, 0.351
Dye 0.4–1.0 Liquid 0.01–100 µsec 1000 5
Nd:YAG 1.06 Solid 0.01–100 µsec 1–100 >100
Ho:YAG 2.1 Solid 1–100 µsec 20 2
Er:YAG 2.94 Solid 5–200 µsec 10 20
CO 2 10.6 Gas 0.01–100 µsec 1000 >100
length (seconds), number of pulses per second (pps), en- length of argon or krypton laser light in blood is also
ergy per pulse ( joules), and average power (watts). Some small. On the other hand, Nd:YAG (λ = 1.06 µm) or GaAs
of the important lasers, which have been used in medicine, (λ = 0.8 µm) laser light is not absorbed well by tissue, and
are given in Tables Ia and Ib. The typical values refer to the extinction length L e is a few millimeters. In the UV,
lasers that are used for medical applications. excimer laser light (λ< 300 nm) is highly absorbed by
both hard tissues and soft tissues, and L e is small.
Inthevisibleorintheinfrared,theabsorbedlaserenergy
B. The Use of Various Lasers in Medicine
is often converted into heat. For low laser incidence (in-
As a laser beam impinges on biological tissue, its energy cident energy per unit area), tissue is moderately heated.
is attenuated in the tissue, due to scattering and to ab- This may give rise to therapeutic heating (such as laser
sorption. In the absorption process, the energy is trans- induced thermal therapy) or to the coagulation of blood.
formed to another form of energy—often to heat. The For high incidence, the tissue vaporizes. In most cases it is
Beer–Lambert law gives the attenuation due to absorp- water that boils away. In practice the laser beam is focused
tion in general. For every tissue and every wavelength λ on a certain area, and the vaporization removes tissue from
there is an absorption coefficient a λ , and one could then this area. The absorption of high intensity laser pulses may
write I λ = I λ (0) exp(−xa λ ), for a tissue thickness x.For give rise to mechanical effects, such as the generation of
wavelength λ, and for L e = 4.6/a λ (cm), I λ (L e ) = I λ (0) shock waves. These may be used for the removal of hard
exp[−a λ (4.6/a λ )] = 0.01 I λ (0), so that 99% of the light tissues, such as gallbladder or urinary stones. The com-
is absorbed after traveling L e = 4.6/a λ cm in tissue. L e is mon medical lasers are bulky and heavy. The output laser
the extinction length. beam is often delivered to a desired spot via an articulat-
Absorption of laser light in tissues and in biological ing arm. This is a system of mirrors, attached to a distal
fluids depends on the characteristic absorption of water, hand piece, which includes a focusing lens. This articu-
hemoglobin, melanin, keratin, and protein. Soft tissues lating arm enables the user to focus the beam and to move
contain a very high percentage of water. Water does not it from place to place. By moving the beam the physician
absorb in the visible, but the absorption is high in the can ablate tissue or perform an incision or an excision
(e.g., laser surgery). Tissues outside the area of the focal
deep UV and the middle IR (λ> 2.8 µm). For the CO 2
laser (λ = 10.6 µm), the extinction length L e is less than spot are also affected. They heat up to a temperature that
0.1 mm. The same is true for the CO laser (λ = 5 µm) and is dependent on the thermal diffusivity and the extinction
for Er:YAG (λ = 2.94 µm). Red pigment in hemoglobin length of the tissue. The heating effect may cause damage
absorbs blue-green light, and therefore the extinction to surrounding tissue. The damage is lower if one uses