Page 75 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioTechnology
P. 75
P1: GRB Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002G-67 May 25, 2001 20:8
Bioreactors 257
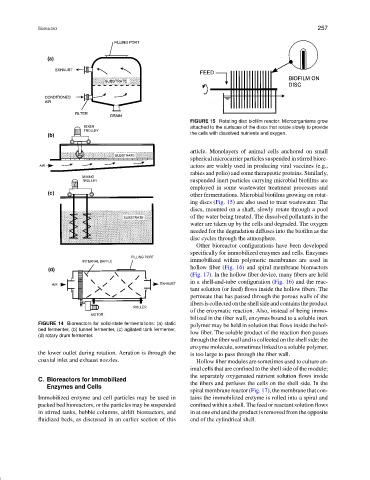
FIGURE 15 Rotating disc biofilm reactor. Microorganisms grow
attached to the surfaces of the discs that rotate slowly to provide
the cells with dissolved nutrients and oxygen.
article. Monolayers of animal cells anchored on small
spherical microcarrier particles suspended in stirred biore-
actors are widely used in producing viral vaccines (e.g.,
rabies and polio) and some therapeutic proteins. Similarly,
suspended inert particles carrying microbial biofilms are
employed in some wastewater treatment processes and
other fermentations. Microbial biofilms growing on rotat-
ing discs (Fig. 15) are also used to treat wastewater. The
discs, mounted on a shaft, slowly rotate through a pool
of the water being treated. The dissolved pollutants in the
water are taken up by the cells and degraded. The oxygen
needed for the degradation diffuses into the biofilm as the
disc cycles through the atmosphere.
Other bioreactor configurations have been developed
specifically for immobilized enzymes and cells. Enzymes
immobilized within polymeric membranes are used in
hollow fiber (Fig. 16) and spiral membrane bioreactors
(Fig. 17). In the hollow fiber device, many fibers are held
in a shell-and-tube configuration (Fig. 16) and the reac-
tant solution (or feed) flows inside the hollow fibers. The
permeate that has passed through the porous walls of the
fibers is collected on the shell side and contains the product
of the enzymatic reaction. Also, instead of being immo-
bilized in the fiber wall, enzymes bound to a soluble inert
FIGURE 14 Bioreactors for solid-state fermentations: (a) static
polymer may be held in solution that flows inside the hol-
bed fermenter, (b) tunnel fermenter, (c) agitated tank fermenter,
(d) rotary drum fermenter. low fiber. The soluble product of the reaction then passes
through the fiber wall and is collected on the shell side; the
enzyme molecule, sometimes linked to a soluble polymer,
the lower outlet during rotation. Aeration is through the is too large to pass through the fiber wall.
coaxial inlet and exhaust nozzles. Hollow fiber modules are sometimes used to culture an-
imal cells that are confined to the shell side of the module;
the separately oxygenated nutrient solution flows inside
C. Bioreactors for Immobilized
the fibers and perfuses the cells on the shell side. In the
Enzymes and Cells
spiral membrane reactor (Fig. 17), the membrane that con-
Immobilized enzyme and cell particles may be used in tains the immobilized enzyme is rolled into a spiral and
packed bed bioreactors, or the particles may be suspended confined within a shell. The feed or reactant solution flows
in stirred tanks, bubble columns, airlift bioreactors, and in at one end and the product is removed from the opposite
fluidized beds, as discussed in an earlier section of this end of the cylindrical shell.