Page 76 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioTechnology
P. 76
P1: GRB Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002G-67 May 25, 2001 20:8
258 Bioreactors
FIGURE 16 Hollow fiber membrane bioreactor.
III. CONSIDERATIONS FOR
BIOREACTOR DESIGN
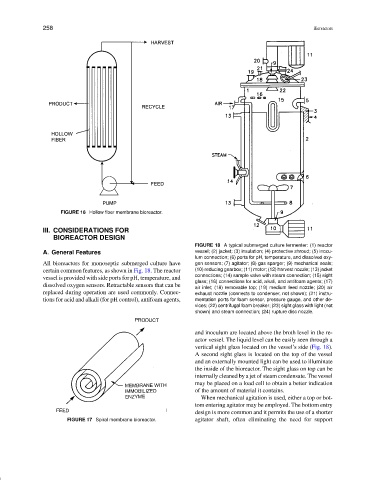
FIGURE 18 A typical submerged culture fermenter: (1) reactor
A. General Features vessel; (2) jacket; (3) insulation; (4) protective shroud; (5) inocu-
lum connection; (6) ports for pH, temperature, and dissolved oxy-
All bioreactors for monoseptic submerged culture have gen sensors; (7) agitator; (8) gas sparger; (9) mechanical seals;
certain common features, as shown in Fig. 18. The reactor (10) reducing gearbox; (11) motor; (12) harvest nozzle; (13) jacket
connections; (14) sample valve with steam connection; (15) sight
vessel is provided with side ports for pH, temperature, and
glass; (16) connections for acid, alkali, and antifoam agents; (17)
dissolved oxygen sensors. Retractable sensors that can be
air inlet; (18) removable top; (19) medium feed nozzle; (20) air
replaced during operation are used commonly. Connec- exhaust nozzle (connects to condenser, not shown); (21) instru-
tions for acid and alkali (for pH control), antifoam agents, mentation ports for foam sensor, pressure gauge, and other de-
vices; (22) centrifugal foam breaker; (23) sight glass with light (not
shown) and steam connection; (24) rupture disc nozzle.
and inoculum are located above the broth level in the re-
actor vessel. The liquid level can be easily seen through a
vertical sight glass located on the vessel’s side (Fig. 18).
A second sight glass is located on the top of the vessel
and an externally mounted light can be used to illuminate
the inside of the bioreactor. The sight glass on top can be
internally cleaned by a jet of steam condensate. The vessel
may be placed on a load cell to obtain a better indication
of the amount of material it contains.
When mechanical agitation is used, either a top or bot-
tom entering agitator may be employed. The bottom entry
design is more common and it permits the use of a shorter
FIGURE 17 Spiral membrane bioreactor. agitator shaft, often eliminating the need for support