Page 303 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Chemical Engineering
P. 303
P1: FYK/LPB P2: FPP Final
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN006C-252 June 27, 2001 14:15
Fluid Mixing 103
is that it is not usually known what effect these particular
properties will have on the process participants in a given
process and, thus, it is usually necessary to measure the
process result either full scale in the plant, or in smaller
size systems in pilot plant or laboratory.
To summarize the situation, geometric similarity con-
trols no mixing variable whatsoever. The question is does
that make a difference to the process. In the portion follow-
ing, we will take a look at the ten basic mixing technology
classifications and see what effect these considerations
might have. Added to this is the fact that most industrial
mixing processes involve two or more of the ten mixing
technological classifications and so their interaction be-
tween those technology classification parameters must be
considered to give the overall performance of the mixing
process.
D. What to Do in the Pilot Plant
There are several considerations to bear in mind when
planning a pilot plant program.
1. The pilot tank is blending rich while full scale tanks
are blending poor. This means that relatively
inefficient blending impellers are needed in the pilot
FIGURE 39 Contours of kinetic energy of turbulence.
plant to correspond to the blending efficient impellers
used in the plant.
2. One technique to make the pilot plant unit more
similar to the plant scale unit is to use impellers of
relatively narrow blade width compared to their
traditional blade widths used with commercial
impellers in the plant. This is purposely reducing the
blending performance and improving the shear rate
performance in the pilot plant by using impellers of
relatively narrow blade width. The blade width
cannot be so small that it gets out of proportion to the
process participant particles.
3. Always bear in mind the qualitative relationship with
viscosity is that the full-scale tank will appear to be
less viscous than the pilot plant tank, somewhere in
the range of a factor of 10–50.
4. If it appears that upon a qualitative examination that
the role of circulation time, blend time, and shear rate
may not be important to the process on scaleup, then
go ahead and use geometric similarity on the pilot
plant study and all of these differences noted above
will play no part in the results of the scaleup
prediction. It may be that there are compensating
effects that while circulation time becomes longer and
shear rates become larger, there is a compensating
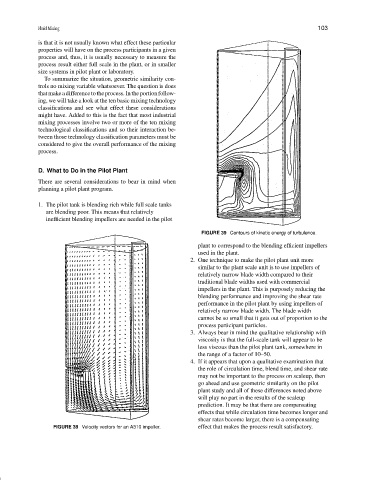
FIGURE 38 Velocity vectors for an A310 impeller. effect that makes the process result satisfactory.