Page 300 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Chemical Engineering
P. 300
P1: FYK/LPB P2: FPP Final
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN006C-252 June 27, 2001 14:15
100 Fluid Mixing
does in a corresponding batch tank. An infinity of mixing
stages is equivalent to a batch tank or to a plug flow reactor.
Usually, however, 5, 10, or 20 stages are sufficient to give a
good efficient reaction time and to possess the advantages
ofcontinuous flowcomparedtothereactiontimeinabatch
system.
A. Inline Mixers
FIGURE 33 Practical heat transfer coefficients for use in estimat-
ing with helical coils and vertical tubes.
Mixers in a flowing pipeline are of two general types,
one utilizing static elements and the other using a rotating
IX. CONTINUOUS FLOW impeller.
A static inline mixer is essentially a device that provides
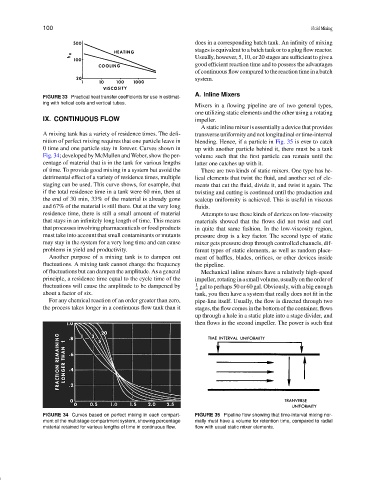
A mixing tank has a variety of residence times. The defi- transverse uniformity and not longitudinal or time-interval
nition of perfect mixing requires that one particle leave in blending. Hence, if a particle in Fig. 35 is ever to catch
0 time and one particle stay in forever. Curves shown in up with another particle behind it, there must be a tank
Fig. 34; developed by McMullen and Weber, show the per- volume such that the first particle can remain until the
centage of material that is in the tank for various lengths latter one catches up with it.
of time. To provide good mixing in a system but avoid the There are two kinds of static mixers. One type has he-
detrimental effect of a variety of residence times, multiple lical elements that twist the fluid, and another set of ele-
staging can be used. This curve shows, for example, that ments that cut the fluid, divide it, and twist it again. The
if the total residence time in a tank were 60 min, then at twisting and cutting is continued until the production and
the end of 30 min, 33% of the material is already gone scaleup uniformity is achieved. This is useful in viscous
and 67% of the material is still there. Out at the very long fluids.
residence time, there is still a small amount of material Attempts to use these kinds of devices on low-viscosity
that stays in an infinitely long length of time. This means materials showed that the flows did not twist and curl
that processes involving pharmaceuticals or food products in quite that same fashion. In the low-viscosity region,
must take into account that small contaminants or mutants pressure drop is a key factor. The second type of static
may stay in the system for a very long time and can cause mixer gets pressure drop through controlled channels, dif-
problems in yield and productivity. ferent types of static elements, as well as random place-
Another purpose of a mixing tank is to dampen out ment of baffles, blades, orifices, or other devices inside
fluctuations. A mixing tank cannot change the frequency the pipeline.
of fluctuations but can dampen the amplitude. As a general Mechanical inline mixers have a relatively high-speed
principle, a residence time equal to the cycle time of the impeller,rotatinginasmallvolume,usuallyontheorderof
fluctuations will cause the amplitude to be dampened by 1 gal to perhaps 50 or 60 gal. Obviously, with a big enough
4
about a factor of six. tank, you then have a system that really does not fitinthe
For any chemical reaction of an order greater than zero, pipe-line itself. Usually, the flow is directed through two
the process takes longer in a continuous flow tank than it stages, the flow comes in the bottom of the container, flows
up through a hole in a static plate into a stage divider, and
then flows in the second impeller. The power is such that
FIGURE 34 Curves based on perfect mixing in each compart- FIGURE 35 Pipeline flow showing that time-interval mixing nor-
ment of the multistage compartment system, showing percentage mally must have a volume for retention time, compared to radial
material retained for various lengths of time in continuous flow. flow with usual static mixer elements.