Page 374 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Chemical Engineering
P. 374
P1: GLQ Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN009K-419 July 19, 2001 20:57
Membranes, Synthetic, Applications 309
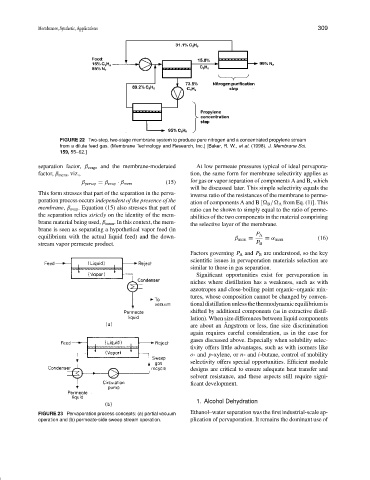
FIGURE 22 Two-step, two-stage membrane system to produce pure nitrogen and a concentrated propylene stream
from a dilute feed gas. (Membrane Technology and Research, Inc.) [Baker, R. W., et al. (1998). J. Membrane Sci.
159, 55–62.]
separation factor, β evap , and the membrane-moderated At low permeate pressures typical of ideal pervapora-
factor, β mem , viz., tion, the same form for membrane selectivity applies as
β pervap = β evap · β mem (15) for gas or vapor separation of components A and B, which
will be discussed later. This simple selectivity equals the
This form stresses that part of the separation in the perva- inverse ratio of the resistances of the membrane to perme-
poration process occurs independent of the presence of the ation of components A and B [ B / A from Eq. (1)]. This
membrane, β evap . Equation (15) also stresses that part of ratio can be shown to simply equal to the ratio of perme-
the separation relies strictly on the identity of the mem- abilities of the two components in the material comprising
brane material being used, β mem . In this context, the mem- the selective layer of the membrane.
brane is seen as separating a hypothetical vapor feed (in
equilibrium with the actual liquid feed) and the down- β mem = P A = α mem (16)
stream vapor permeate product. P B
Factors governing P A and P B are understood, so the key
scientific issues in pervaporation materials selection are
similar to those in gas separation.
Significant opportunities exist for pervaporation in
niches where distillation has a weakness, such as with
azeotropes and close-boiling point organic–organic mix-
tures, whose composition cannot be changed by conven-
tional distillation unless the thermodynamic equilibrium is
shifted by additional components (as in extractive distil-
lation). When size differences between liquid components
˚
are about an Angstrom or less, fine size discrimination
again requires careful consideration, as in the case for
gases discussed above. Especially when solubility selec-
tivity offers little advantages, such as with isomers like
o- and p-xylene, or n- and i-butane, control of mobility
selectivity offers special opportunities. Efficient module
designs are critical to ensure adequate heat transfer and
solvent resistance, and these aspects still require signi-
ficant development.
1. Alcohol Dehydration
FIGURE 23 Pervaporation process concepts: (a) partial vacuum Ethanol–water separation was the first industrial-scale ap-
operation and (b) permeate-side sweep stream operation. plication of pervaporation. It remains the dominant use of