Page 85 - Engineered Interfaces in Fiber Reinforced Composites
P. 85
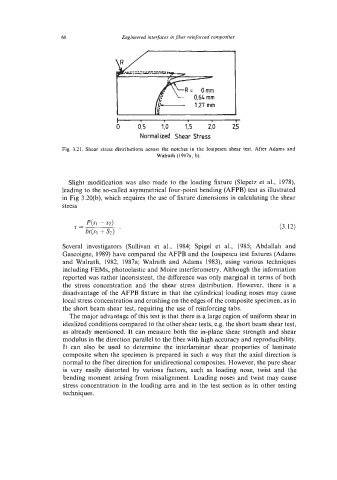
68 Engineered interfaces in fiber reinforced composites
1 1 I I
0 0.5 l,o 1,s 2,o 25
Normalized Shear Stress
Fig. 3.21. Shear stress distributions across the notches in the Iosipescu shear test. After Adams and
Walrath (1987a, b).
Slight modification was also made to the loading fixture (Slepetz et al., 1978),
leading to the so-called asymmetrical four-point bending (AFPB) test as illustrated
in Fig 3.20(b), which requires the use of fixture dimensions in calculating the shear
stress
(3.12)
Several investigators (Sullivan et al., 1984; Spigel et al., 1985; Abdallah and
Gascoigne, 1989) have compared the AFPB and the Iosipescu test fixtures (Adams
and Walrath, 1982, 1987a; Walrath and Adams 1983), using various techniques
including FEMs, photoelastic and Moire interferometry. Although the information
reported was rather inconsistent, the difference was only marginal in terms of both
the stress concentration and the shear stress distribution. However, there is a
disadvantage of the AFPB fixture in that the cylindrical loading noses may cause
local stress concentration and crushing on the edges of the composite specimen, as in
the short beam shear test, requiring the use of reinforcing tabs.
The major advantage of this test is that there is a large region of uniform shear in
idealized conditions compared to the other shear tests, e.g. the short beam shear test,
as already mentioned. It can measure both the in-plane shear strength and shear
modulus in the direction parallel to the fiber with high accuracy and reproducibility.
It can also be used to determine the interlaminar shear properties of laminate
composite when the specimen is prepared in such a way that the axial direction is
normal to the fiber direction for unidirectional composites. However, the pure shear
is very easily distorted by various factors, such as loading nose, twist and the
bending moment arising from misalignment. Loading noses and twist may cause
stress concentration in the loading area and in the test section as in other testing
techniques.