Page 93 - Engineered Interfaces in Fiber Reinforced Composites
P. 93
76 Engineered interfaces in fiber reinforced composites
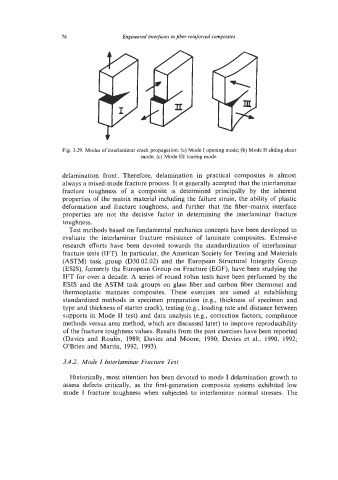
Fig. 3.29. Modes of interlaminar crack propagation: (a) Mode I opening mode; (b) Mode I1 sliding shear
mode; (c) Mode I11 tearing mode.
delamination front. Therefore, delamination in practical composites is almost
always a mixed-mode fracture process. It is generally accepted that the interlaminar
fracture toughness of a composite is determined principally by the inherent
properties of the matrix material including the failure strain, the ability of plastic
deformation and fracture toughness, and further that the fiber-matrix interface
properties are not the decisive factor in determining the interlaminar fracture
toughness.
Test methods based on fundamental mechanics concepts have been developed to
evaluate the interlaminar fracture resistance of laminate composites. Extensive
research efforts have been devoted towards the standardization of interlaminar
fracture tests (IFT). In particular, the American Society for Testing and Materials
(ASTM) task group (D30.02.02) and the European Structural Integrity Group
(ESIS), formerly the European Group on Fracture (EGF), have been studying the
IFT for over a decade. A series of round robin tests have been performed by the
ESIS and the ASTM task groups on glass fiber and carbon fiber thermoset and
thermoplastic matrices composites. These exercises are aimed at establishing
standardized methods in specimen preparation (e.g., thickness of specimen and
type and thickness of starter crack), testing (e.g., loading rate and distance between
supports in Mode I1 test) and data analysis (e.g., correction factors, compliance
methods versus area method, which are discussed later) to improve reproducibility
of the fracture toughness values. Results from the past exercises have been reported
(Davies and Roulin, 1989; Davies and Moore, 1990; Davies et al., 1990, 1992;
O’Brien and Martin, 1992, 1993).
3.4.2. Mode I Interlaminar Fracture Test
Historically, most attention has been devoted to mode I delamination growth to
assess defects critically, as the first-generation composite systems exhibited low
mode I fracture toughness when subjected to interlaminar normal stresses. The