Page 690 - Engineering Digital Design
P. 690
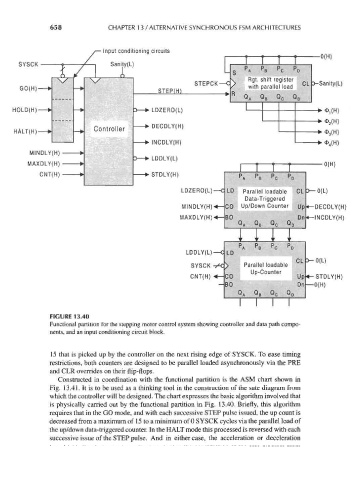
658 CHAPTER 13 / ALTERNATIVE SYNCHRONOUS FSM ARCHITECTURES
Input conditioning circuits
' T i l l 0(H)
* / [ L § ^A K B P C * D
SYSCK ouiiimL; • z ^ - £ »• - -I'""
V
GO(H)- — > o 1 trln ) STEPCK ^> --"- CL " S
STEP.H,
^ o
- W Q. « Q R Q r W Qn
B
U
HOLD(H)- — > -> 3 — ^LDZERO(L) ' +
^DECDLY(H)
Controller I
H
HALT(H) — > HH WUIPIIUIIC ' 1 *3> 3(H)
— *
*
MNCDLY(H) ^(H
' >
DLY(H) *
D — ^LDDLY(L)
DLY(H) *• 0(H)
1 1 1 '
DNT(H) * ^STDLY(H) PA PB p c p D
LDZERO(L) Parallel loadable CL •0(L)
Data-Triggered
MINDLY(H) CO Up/Down Counter Up -DECDLY(H)
MAXDLY(H) BO Do -INCDLY(H)
PA PB P
LDDLY(L)- LD
CL
SYSCK Parallel loadable
Up-Counter
CNT(H) CO r Up -STDLY(H)
BO Dn •0(H)
FIGURE 13.40
Functional partition for the stepping motor control system showing controller and data path compo-
nents, and an input conditioning circuit block.
15 that is picked up by the controller on the next rising edge of SYSCK. To ease timing
restrictions, both counters are designed to be parallel loaded asynchronously via the PRE
and CLR overrides on their flip-flops.
Constructed in coordination with the functional partition is the ASM chart shown in
Fig. 13.41. It is to be used as a thinking tool in the construction of the sate diagram from
which the controller will be designed. The chart expresses the basic algorithm involved that
is physically carried out by the functional partition in Fig. 13.40. Briefly, this algorithm
requires that in the GO mode, and with each successive STEP pulse issued, the up count is
decreased from a maximum of 15 to a minimum of 0 SYSCK cycles via the parallel load of
the up/down data-triggered counter. In the HALT mode this processed is reversed with each
successive issue of the STEP pulse. And in either case, the acceleration or deceleration