Page 720 - Engineering Digital Design
P. 720
686 CHAPTER 14 / ASYNCHRONOUS STATE MACHINE DESIGN AND ANALYSIS
Memory
stage
Output
Intput (OP)
(IP)
Output
forming
Ideal NS
V1 logic
forming
logic
(No delays)
PSfedback \_ Fictitious LPD
memory elements
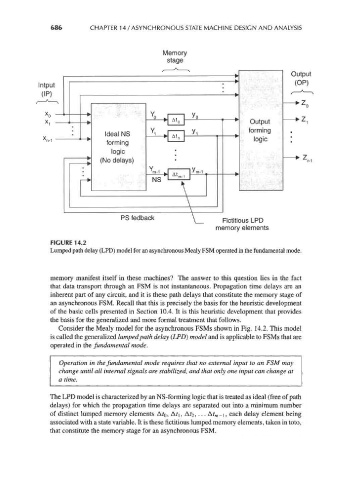
FIGURE 14.2
Lumped path delay (LPD) model for an asynchronous Mealy FSM operated in the fundamental mode.
memory manifest itself in these machines? The answer to this question lies in the fact
that data transport through an FSM is not instantaneous. Propagation time delays are an
inherent part of any circuit, and it is these path delays that constitute the memory stage of
an asynchronous FSM. Recall that this is precisely the basis for the heuristic development
of the basic cells presented in Section 10.4. It is this heuristic development that provides
the basis for the generalized and more formal treatment that follows.
Consider the Mealy model for the asynchronous FSMs shown in Fig. 14.2. This model
is called the generalized lumped path delay (LPD) model and is applicable to FSMs that are
operated in the fundamental mode.
Operation in the fundamental mode requires that no external input to an FSM may
change until all internal signals are stabilized, and that only one input can change at
a time.
The LPD model is characterized by an NS-forming logic that is treated as ideal (free of path
delays) for which the propagation time delays are separated out into a minimum number
of distinct lumped memory elements A?o, At\, A?2, • • • At m-i, each delay element being
associated with a state variable. It is these fictitious lumped memory elements, taken in toto,
that constitute the memory stage for an asynchronous FSM.