Page 759 - Engineering Digital Design
P. 759
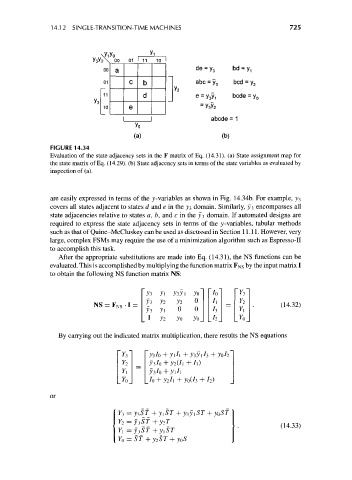
14.12 SINGLE-TRANSITION-TIME MACHINES 725
00 01 I 11 10 I
00 a de = y 3 bd = y 1
01 c b abc = y 3 bed = y.
11 d e = y 3y 1 bcde = y 0
10 e = y y
3 2
abcde = 1
(a) (b)
FIGURE 14.34
Evaluation of the state adjacency sets in the F matrix of Eq. (14.31). (a) State assignment map for
the state matrix of Eq. (14.29). (b) State adjacency sets in terms of the state variables as evaluated by
inspection of (a).
are easily expressed in terms of the y-variables as shown in Fig. 14.34b. For example, ^3
covers all states adjacent to states d and e in the y 3 domain. Similarly, y 3 encompasses all
state adjacencies relative to states a, b, and c in the 3/3 domain. If automated designs are
required to express the state adjacency sets in terms of the y-variables, tabular methods
such as that of Quine-McCluskey can be used as discussed in Section 11.11. However, very
large, complex FSMs may require the use of a minimization algorithm such as Espresso-II
to accomplish this task.
After the appropriate substitutions are made into Eq. (14.31), the NS functions can be
evaluated. This is accomplished by multiplying the function matrix FNS by the input matrix I
to obtain the following NS function matrix NS:
J3 y\
o
y 2
y 3 y 2
= F NS .I= (14-32)
y 3 yi 0 0
l y 2 yo yo Y
By carrying out the indicated matrix multiplication, there results the NS equations
"y 3/o + yi/i + y 3y\I 3 +
Y 2 '
Y 0
or
y 0ST
+y 2T
(14.33)
y, =y 3sf