Page 770 - Engineering Digital Design
P. 770
736 CHAPTER 14/ASYNCHRONOUS STATE MACHINE DESIGN AND ANALYSIS
S+T
Sanity
\ST ' I
Q,X 00 01 11 10 P Q
ST
ST
ST
•• S " / ^~~/
S+T
(a) (b)
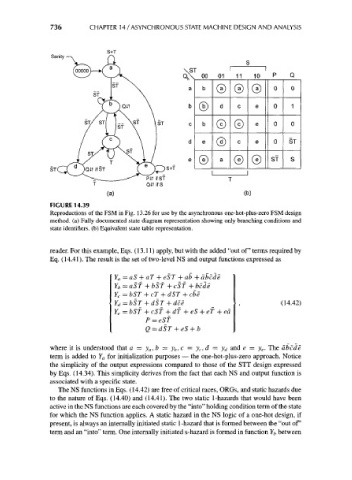
FIGURE 14.39
Reproductions of the FSM in Fig. 13.26 for use by the asynchronous one-hot-plus-zero FSM design
method, (a) Fully documented state diagram representation showing only branching conditions and
state identifiers, (b) Equivalent state table representation.
reader. For this example, Eqs. (13.11) apply, but with the added "out of" terms required by
Eq. (14.41). The result is the set of two-level NS and output functions expressed as
Y a = aS + aT + eST + ab + abode
Y b=aST + bST + cST + bcde
Y c = bST +cT + dST + cbe
(14.42)
Y e = bST + cST + dT + eS + eT + ea
= eST
= dST + eS + b
where it is understood that a = y a,b — y/,, c = y c,d = y d and e = y e. The abode
term is added to Y a for initialization purposes — the one-hot-plus-zero approach. Notice
the simplicity of the output expressions compared to those of the STT design expressed
by Eqs. (14.34). This simplicity derives from the fact that each NS and output function is
associated with a specific state.
The NS functions in Eqs. (14.42) are free of critical races, ORGs, and static hazards due
to the nature of Eqs. (14.40) and (14.41). The two static 1-hazards that would have been
active in the NS functions are each covered by the "into" holding condition term of the state
for which the NS function applies. A static hazard in the NS logic of a one-hot design, if
present, is always an internally initiated static 1-hazard that is formed between the "out of"
term and an "into" term. One internally initiated s-hazard is formed in function Yb between